Guide: How to build your own investable universe

Investing is A Wealth Creation Machine
Investing is a powerful tool for building wealth over the long term. It's the reason you're here, reading this guide, with a commitment to creating long-term value.
Despite the numerous reasons to sell—market fluctuations, economic downturns, or personal financial needs—historical data shows that markets tend to grow over time.
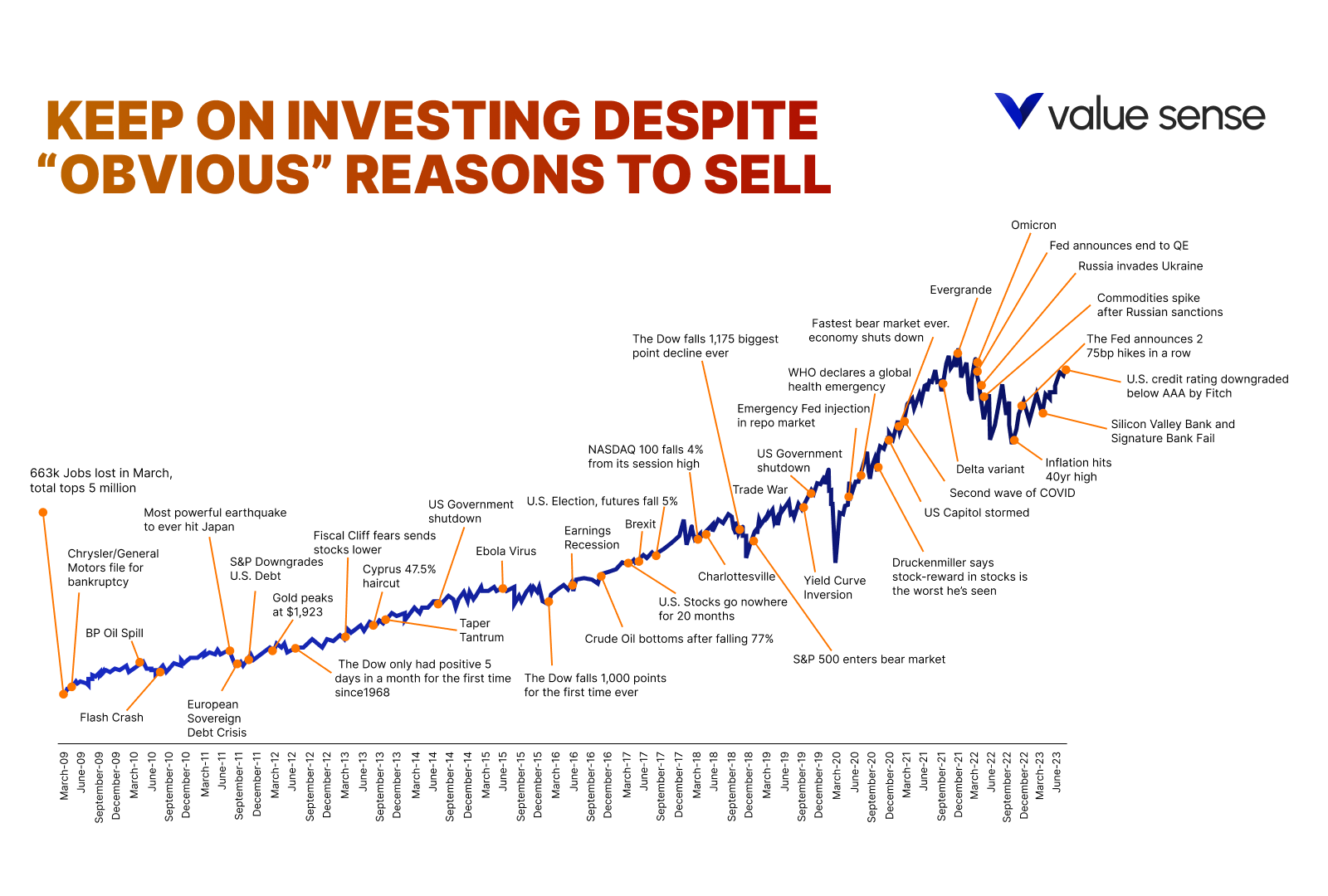
The stock market's inherent upward trend means that, on average, it rises more than it falls.
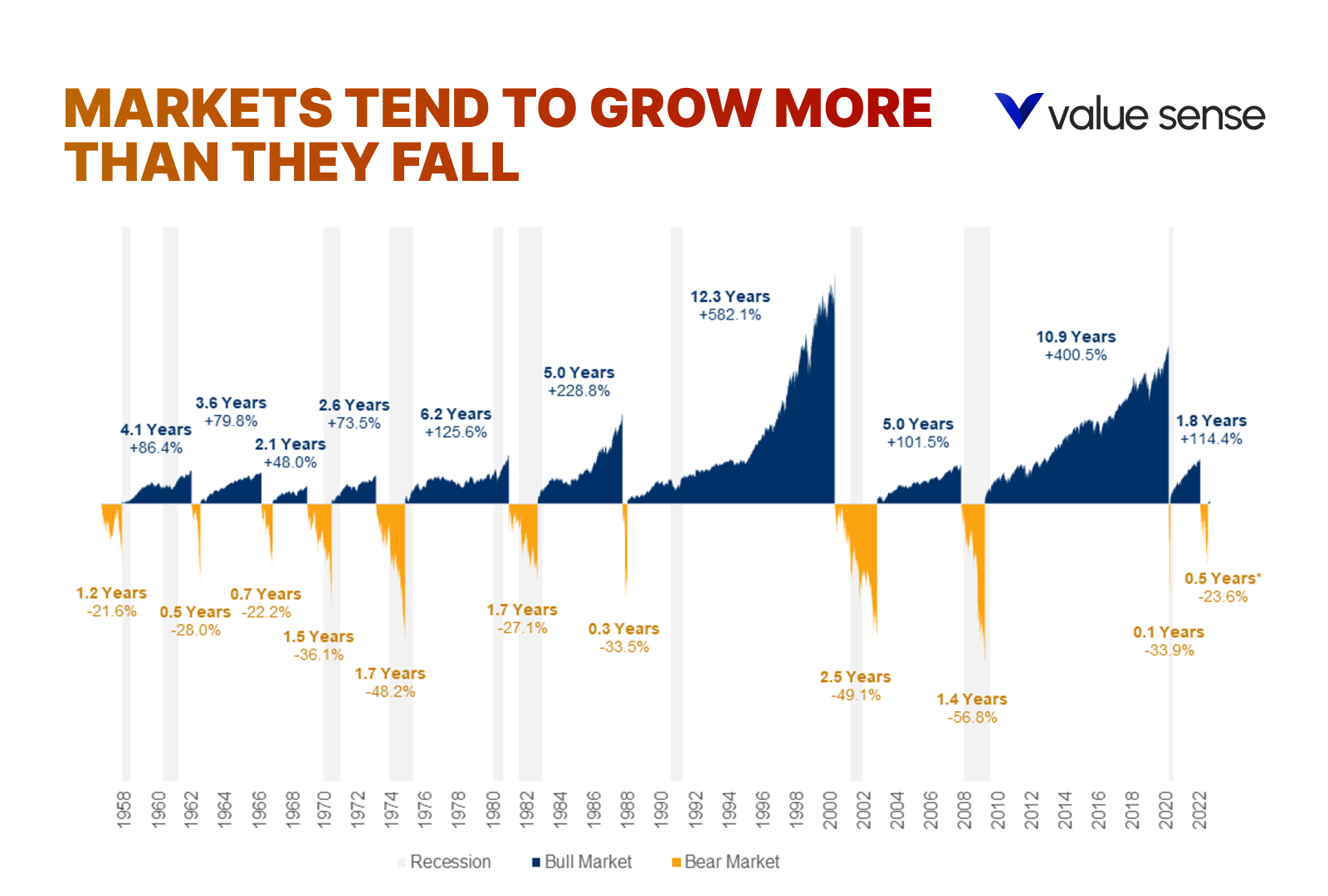
By understanding this fundamental principle, you can maintain a long-term perspective and resist the urge to make impulsive decisions based on short-term market movements.
2. Stock Picking Can Yield Great Results, But It's Not for Everyone
Stock picking, the practice of choosing individual stocks in the hope of outperforming the market, can deliver outstanding returns for some investors. Certain companies have the potential to provide exceptional growth, leading to significant gains.
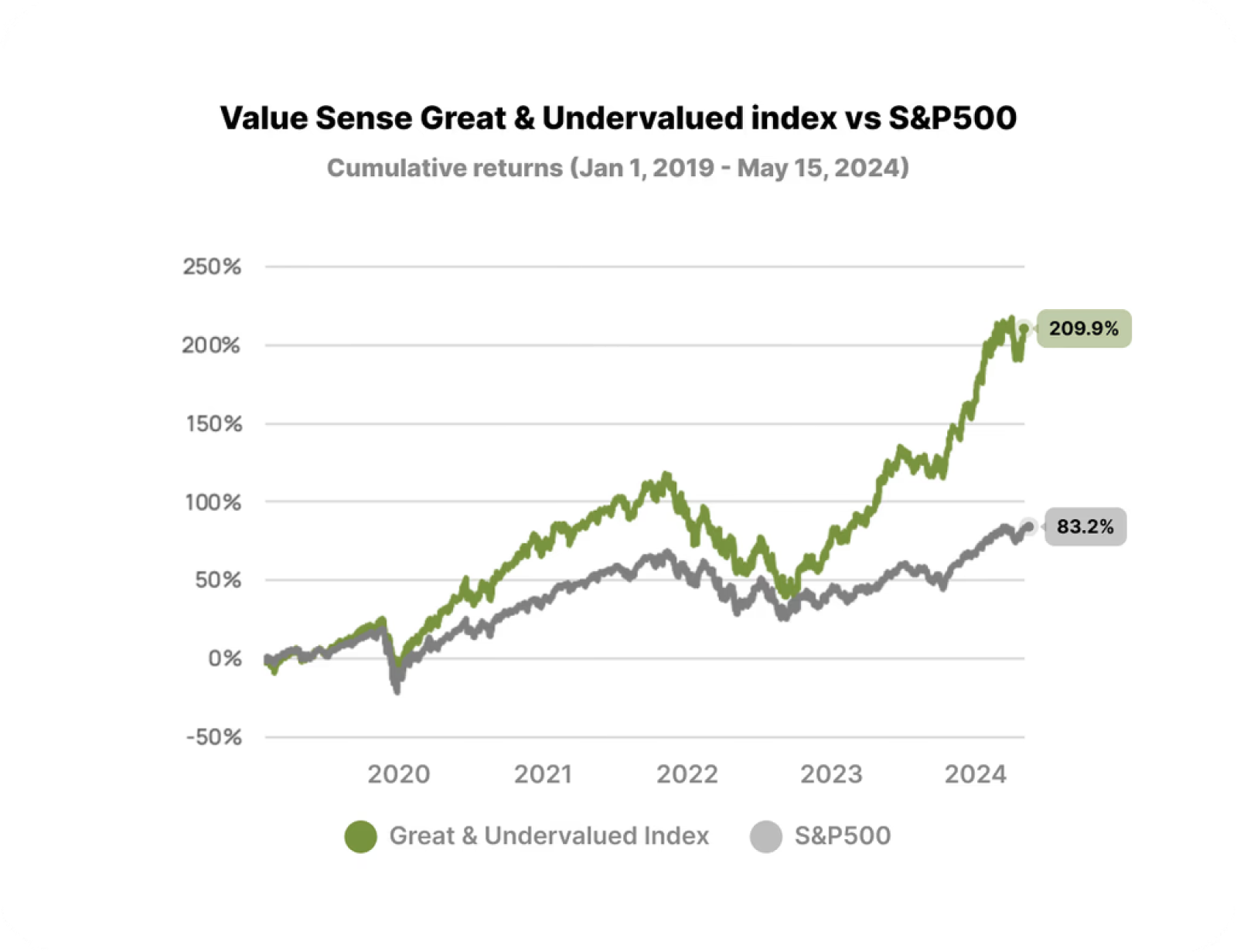
However, it's essential to recognize that stock picking is inherently risky. Many other companies can lead to substantial losses if not carefully selected.
The performance of individual stocks often follows a power law distribution, where a small number of stocks deliver outsized returns while many underperform or lose value. You don’t need to pick a lot of winners, a few of them will do it for your investment returns.
Best part here is that with the right approach you can select these winners.
3. Even Funds Lose Money Despite Being Managed by Professionals
Even professional fund managers, with their extensive resources and expertise, can experience losses.
A notable example is Warren Buffett's famous bet against hedge funds, where he wagered that an S&P 500 index fund would outperform a basket of hedge funds over ten years.
The takeaway from this bet is not that stock picking is ineffective, but rather that many funds suffer from short-term thinking and high fees that erode returns. Buffett's victory underscores the importance of a long-term perspective and low-cost investing.
4. Stock Picking Works If You Have a System and Stick to It
Stock picking can be effective if you have a well-defined system and adhere to it consistently.
Various investment systems exist, each with its own set of rules and criteria for selecting stocks.
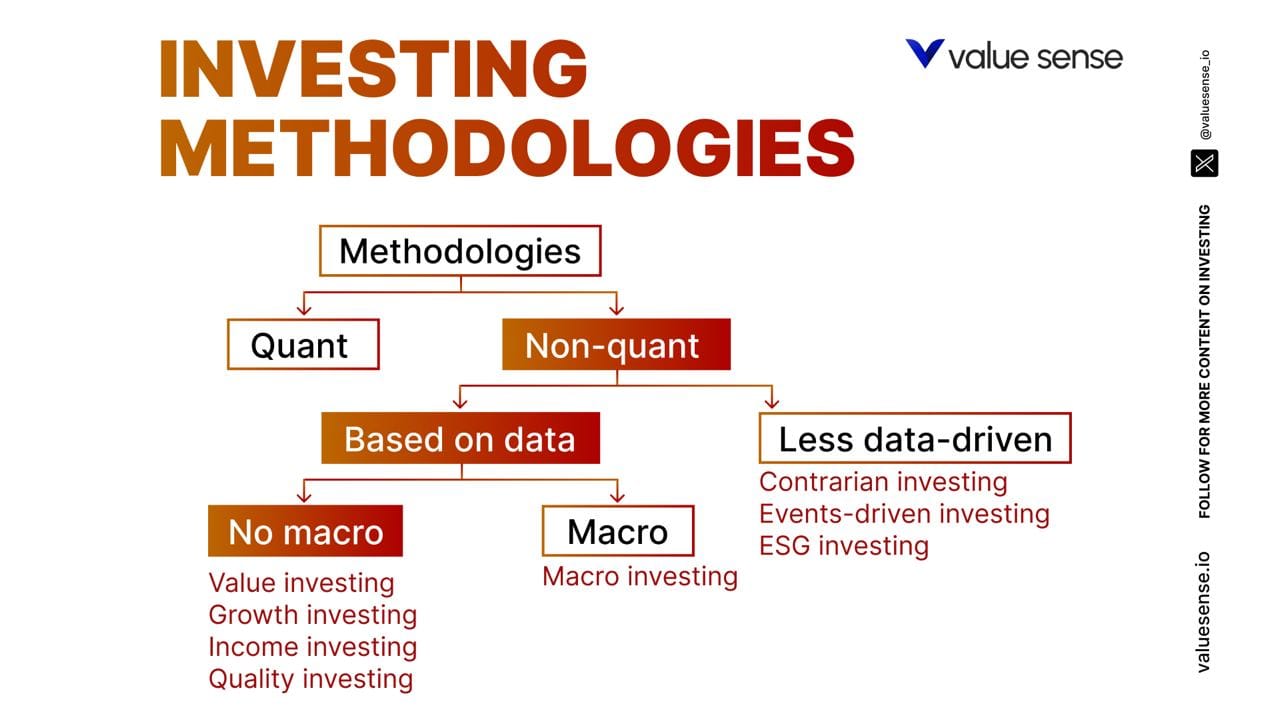
For instance, value investing, popularized by investors Ben Graham and Warren Buffett, focuses on buying undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals.
Terry Smith popularized quality investing, where he carefully selects companies that turned out to be champions in their industries and tries to buy them at reasonable prices.
These investors follow robust systems and principles that guide their decisions. Even Buffett has evolved his system over time to adapt to changing market conditions and maintain its effectiveness.
By establishing and following your own system, you can improve your chances of success in stock picking.
5. Why Can't We Do It Too?
You, too, can develop and follow an investment system.
A well-structured system helps make investment behaviors automatic, reducing the influence of emotions and biases.
By adhering to a set of principles, you can maintain discipline and consistency in your investment decisions. Combining the wisdom of successful investors with modern analytical methods allows you to create a personalized investment approach.
This approach leverages proven strategies while incorporating modern tools like Value Sense and techniques to enhance your decision-making process.
6. Why Great Investors Can Do This and You Can Too
Great investors have access to advanced tools and resources, such as Bloomberg terminals, that provide comprehensive market data and analysis.
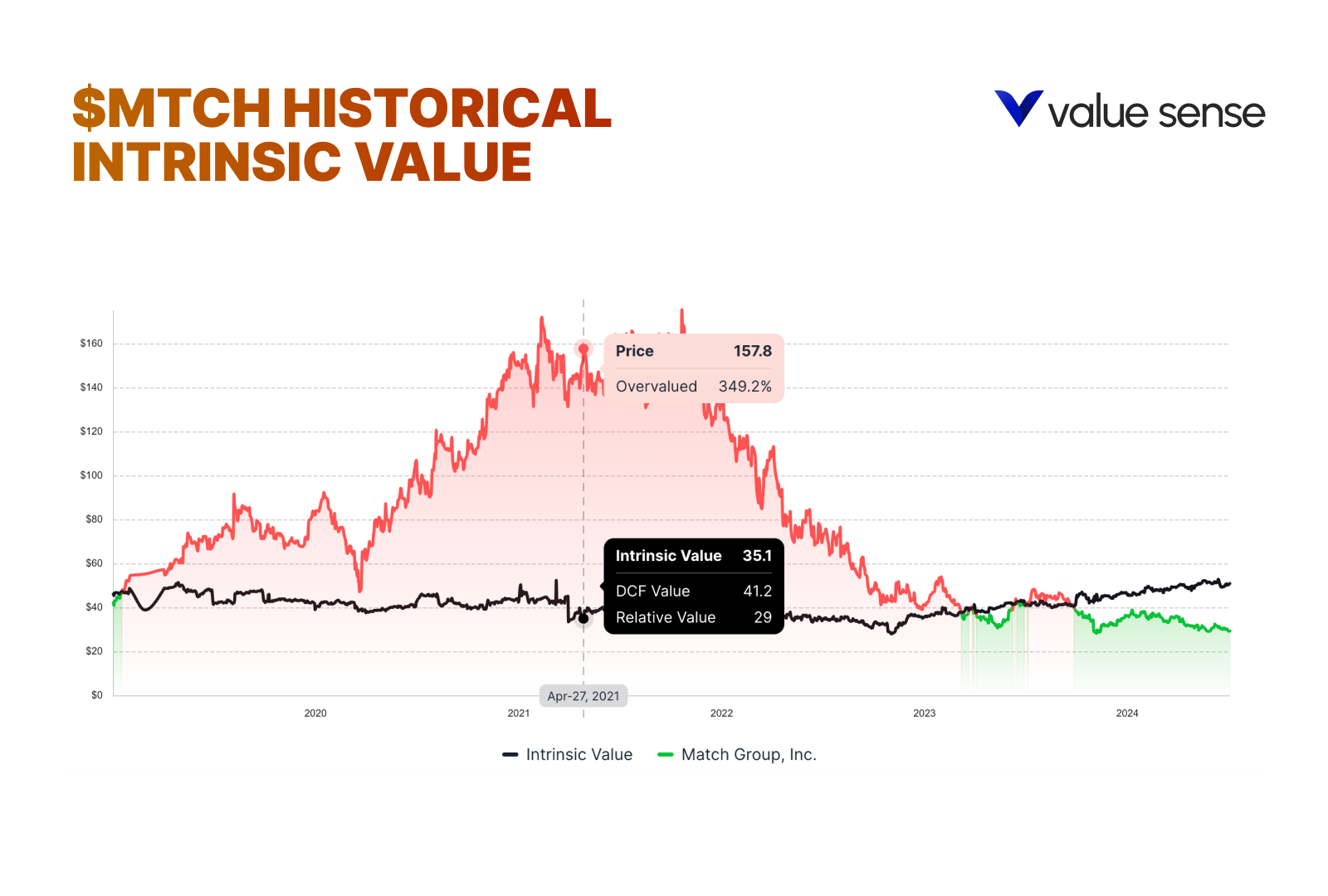
These tools enable them to assess the quality of companies and determine their intrinsic value.
However, with the advent of sophisticated analytical engines and investment platforms, retail investors can now access similar capabilities. While professional funds spend significant amounts on research and data, retail investors can use modern tools to level the playing field (e.g. Value Sense provides you with the necessary analytical engine to identify high-quality companies and their fundamental value.
7. Define Your Investment Approach
To build your investable universe, start by defining your investment approach.
You can choose between:
- quantitative-first approach
- a qualitative-first approach
- or a combined approach
A quantitative-first approach focuses on numerical metrics and data-driven criteria, while a qualitative-first approach emphasizes understanding the business and its qualitative aspects.
A combined approach integrates both quantitative and qualitative analysis to provide a comprehensive evaluation of potential investments.
8. Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis involves using numerical metrics to screen and evaluate potential investments. Key metrics to consider include:
- Return on invested capital (ROIC) > 15%:
- Indicates efficient use of capital to generate returns.
- Revenue growth > 7%:
- Consistent revenue growth signifies a company's ability to expand.
- Net income margin > 20%:
- High-profit margins show operational efficiency.
- Gross margin > 40%:
- Indicates strong pricing power and cost management.
- Net debt / EBITDA < 3.0x:
- Low leverage suggests financial stability.
- Interest coverage > 5.0x:
- Ensures the company can comfortably cover its interest obligations.
- Free cash flow (FCF) / EBITDA > 70%:
- High free cash flow relative to EBITDA shows good cash generation capabilities.
- Free cash flow yield > 3%:
- This ratio indicates the cash return on the company's equity value.
These metrics serve as screening criteria to identify companies with strong financial fundamentals and growth potential.
9. Qualitative Criteria
In addition to quantitative analysis, qualitative criteria play a crucial role in evaluating potential investments. Consider the following factors:
- Understanding the Business
- Assess the company's business model, products, and services
- Determine if the business has a sustainable competitive advantage.
- Risk Assessment:
- Identify potential risks, including market competition, regulatory challenges, and operational risks
- Evaluate how the company manages these risks.
- Competitive Moat:
- Determine if the company has a durable competitive advantage that protects it from competitors
- This could include brand strength, patents, or network effects.
- Management Quality:
- Evaluate the experience, track record, and integrity of the company's management team
- Skin in the game, how much equity does the management own
- Strong leadership is crucial for long-term success.
By integrating qualitative criteria into your analysis, you can gain a deeper understanding of the company's potential for sustainable growth.
10. Build and Refine Your Screening Criteria
Once you have defined your quantitative and qualitative criteria, build and refine your screening process.
Use screening tools and software to filter stocks based on your criteria. Regularly backtest your screening criteria to ensure their effectiveness.
Backtesting involves applying your criteria to historical data to evaluate how well they would have predicted past performance. This process helps refine your criteria and improve the accuracy of your stock selection.
11. Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment
Building an investable universe is not a one-time task.
Continuous monitoring and adjustment are essential to maintain the quality of your investments. Regularly review your portfolio and make adjustments based on changes in market conditions, company performance, and new information.
Stay informed about industry trends and economic developments that may impact your investments.
Don’t forget to check out earnings reports from companies in your investable universe
By continuously monitoring and adjusting your portfolio, you can ensure that it remains aligned with your investment goals and criteria.
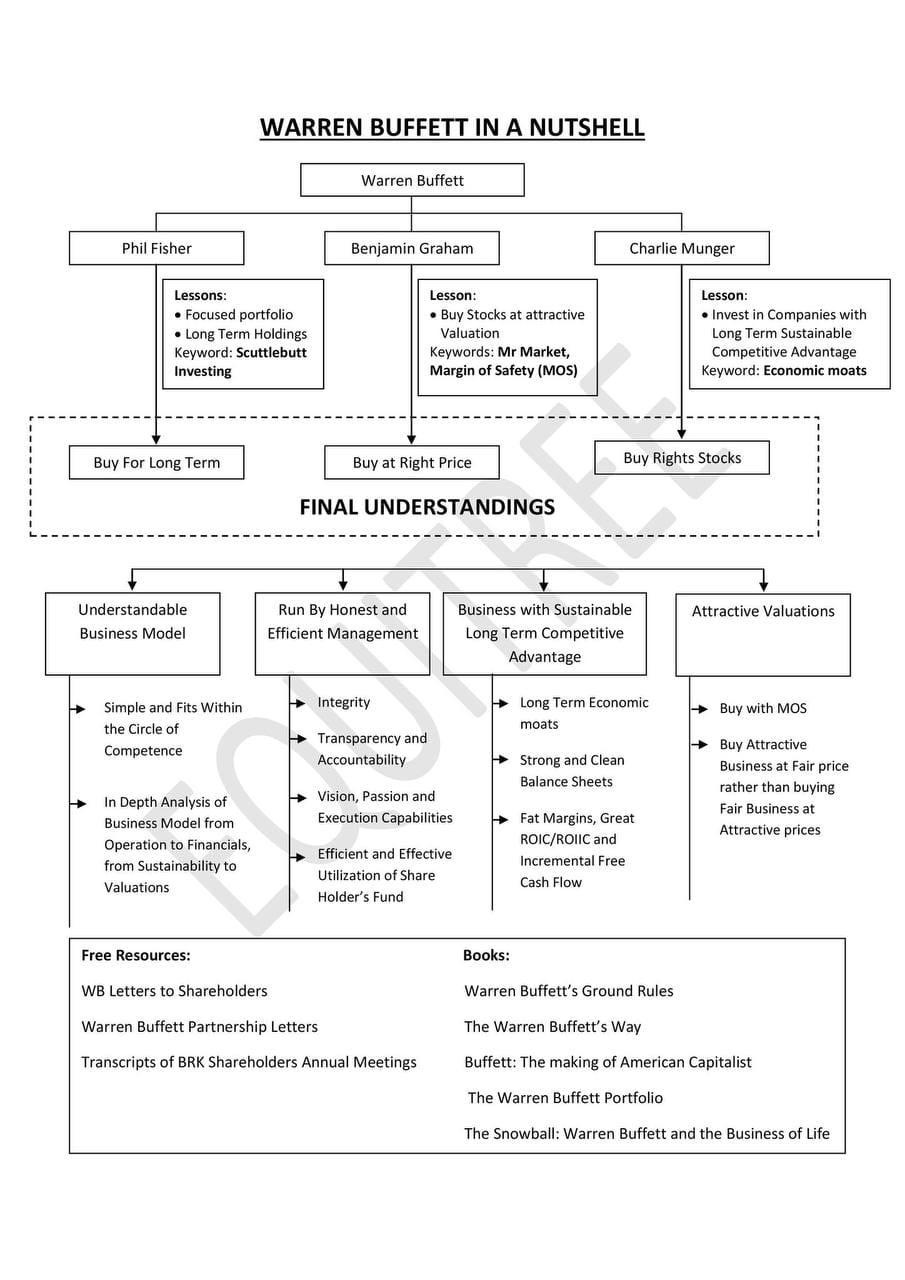
12. Investment Systems of Great Investors
To further enhance your investment strategy, study the systems of great investors. Here are a few notable examples:
- Warren Buffett: Known for his value investing approach, Buffett focuses on buying undervalued companies with strong fundamentals and holding them for the long term.
- Terry Smith: Smith's investment philosophy emphasizes buying high-quality companies with strong returns on capital and holding them indefinitely.
- Monish Pabrai: Pabrai follows a value investing approach inspired by Buffett, focusing on buying undervalued stocks and maintaining a concentrated portfolio.
By studying the systems of these successful investors, you can gain insights into their strategies and apply similar principles to your own investment approach.
As a bonus here is the list of high-quality companies that you may add to your watchlist. With Value Sense you can instantly identify their quality and intrinsic value:
- Microsoft
- Visa
- Mastercard
- Idexx Laboratories
- Constellation Software
- Apple
- Applied Materials
- NVR
- Pool Corp
- Watsco
- Adobe
- Cadence Design Systems
- Fortinet
- Copart
- Old Dominion Freight Line
- West Pharma Services
- Alimentation Couche-Tard
- Canadian Pacific Railway
- Costco
- MSCI
- Mettler Toledo
- Moody’s
- S&P Global
- Ulta Beauty
- Texas Instrument
- Zoetis
- Xpel
- Paycom
- Amazon
- ANSYS
- Automatic Data Processing
- Autozone
- Blackrock
- Brown & Brown
- Booking Holdings
- Broadcom
- Cintas
- Colgate-Palmolive
- Coca-Cola
- Danaher
- Dollar General
- Edwards Lifesciences
- Eli Lilly
- Estee Lauder
- Factset Research
- Fair Isaac
- Heico
- Hershey
- Home Depot
- Intercontinental Exchange
- Intuit
- Jack Henry
- Johnson & Johnson
- KLA Corp.
- McDonald’s
- Monster Beverage
- Nasdaq
- Nike
- Nvidia
- O’Reilly Automotive
- Paychex
- Pepsico
- Procter & Gamble
- Qualcomm
- Roper Technologies
- Sherwin Williams
- Synopsys
- Thermo Fisher
- Tractor Supply
- TransDigm Group
- TransUnion Group
- United Health
- Veeva Systems
- Verisign
- Waste Management
- Williams Sonoma
- Landstar Systems
- Ufp Industries
- Qualys
- CarMax

