Top Dividend Stocks for 2025: Investor Favorites Revealed

Welcome to Value Sense Blog
At Value Sense, we provide insights on the stock market, intrinsic value tools, and stock ideas with undervalued companies. You can explore our research products at valuesense.io and learn more about our approach on our site.
With 2025 shaping up to be a potentially sideways market, dividend stocks are gaining renewed attention from those seeking steady cash flow and stability. We've compiled the most popular dividend stock picks based on a recent investor discussion, analyzing yields, stability, and growth potential.
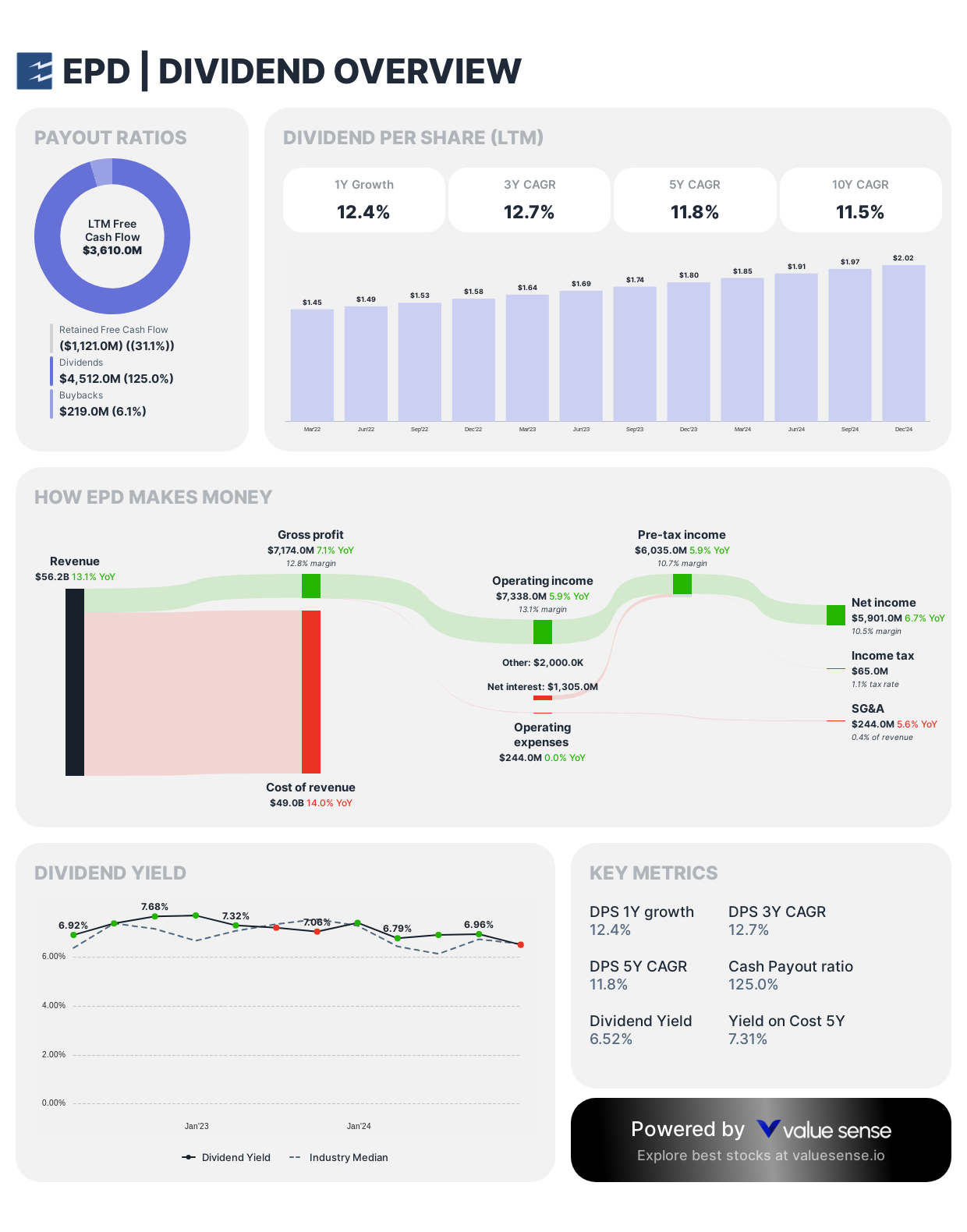
Enterprise Products Partners (EPD)
EPD earned multiple recommendations for its combination of high yield and growth potential.
Dividend Framework: As a midstream master limited partnership (MLP), Enterprise Products Partners structures its dividend policy around distributable cash flow, delivering exceptional yield through quarterly distributions with consistent sequential increases spanning over 20 years.
Strategic Considerations:
- Distribution coverage ratio maintained above 1.6x for financial resilience
- Deliberately measured distribution growth rate (~3-5%) prioritizing sustainability
- Tax-advantaged structure enhances effective investor returns
Investor Implications: Enterprise's distribution policy exemplifies disciplined midstream infrastructure management, balancing substantial current income with prudent reinvestment in fee-based energy transportation and processing assets, offering relatively low correlation to energy commodity price fluctuations.
Important tax consideration: EPD issues a K-1 form for tax purposes and may not be ideal for retirement accounts. Some investors prefer holding it in taxable accounts.
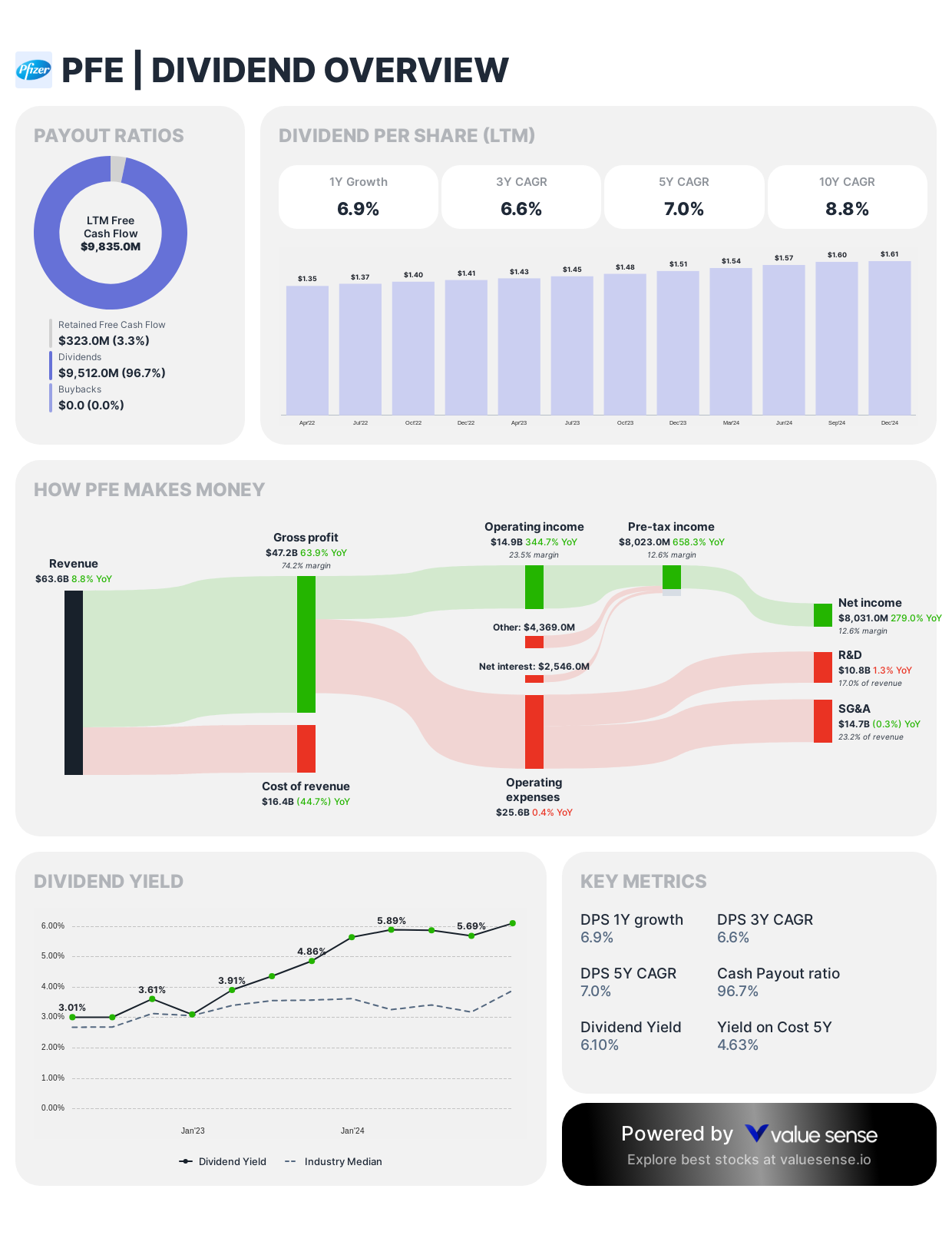
Pfizer (PFE)
Pfizer emerged as a surprisingly popular choice, with multiple investors expressing confidence in its prospects for 2025 and beyond.
Dividend Framework: Pfizer implements a balanced dividend approach balancing income generation with strategic flexibility, characterized by steady increases following significant portfolio realignments in recent years.
Strategic Considerations:
- Dividend reset following Upjohn segment divestiture
- Current yield positioned competitively within pharmaceutical sector
- Post-pandemic cash deployment prioritizes dividend sustainability alongside M&A opportunities
Investor Implications: Pfizer's dividend strategy demonstrates methodical capital allocation balancing immediate shareholder returns with acquisition firepower, leveraging COVID-19 revenue to strengthen both dividend foundation and future growth initiatives.
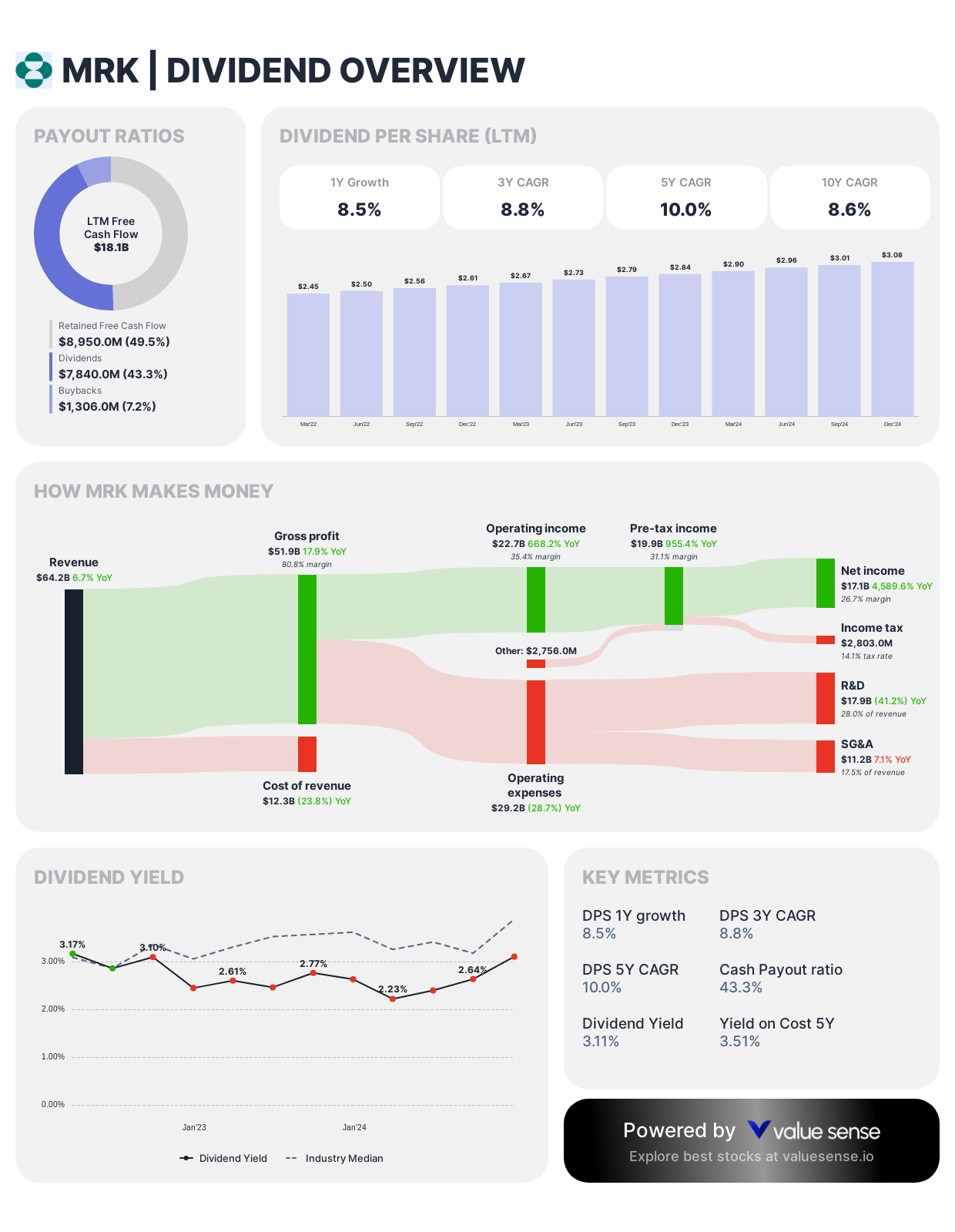
Merck (MRK)
One investor specifically highlighted Merck as an opportunity, market is very bearish on them due to China vaccines and Keytruda issues.
Dividend Framework: Merck employs a conservative dividend strategy prioritizing financial flexibility for R&D investment and strategic acquisitions while maintaining modest but reliable income for shareholders.
Strategic Considerations:
- Modest annual increases with below-average pharmaceutical sector yield
- Deliberately restrained payout ratio (~45-50%)
- Dividend increases calibrated to maintain equilibrium between shareholder returns and pipeline investment
Investor Implications: Merck's dividend policy signals management's prioritization of sustainable long-term growth through pipeline advancement rather than maximizing near-term shareholder distributions, reflecting the capital-intensive nature of pharmaceutical innovation.
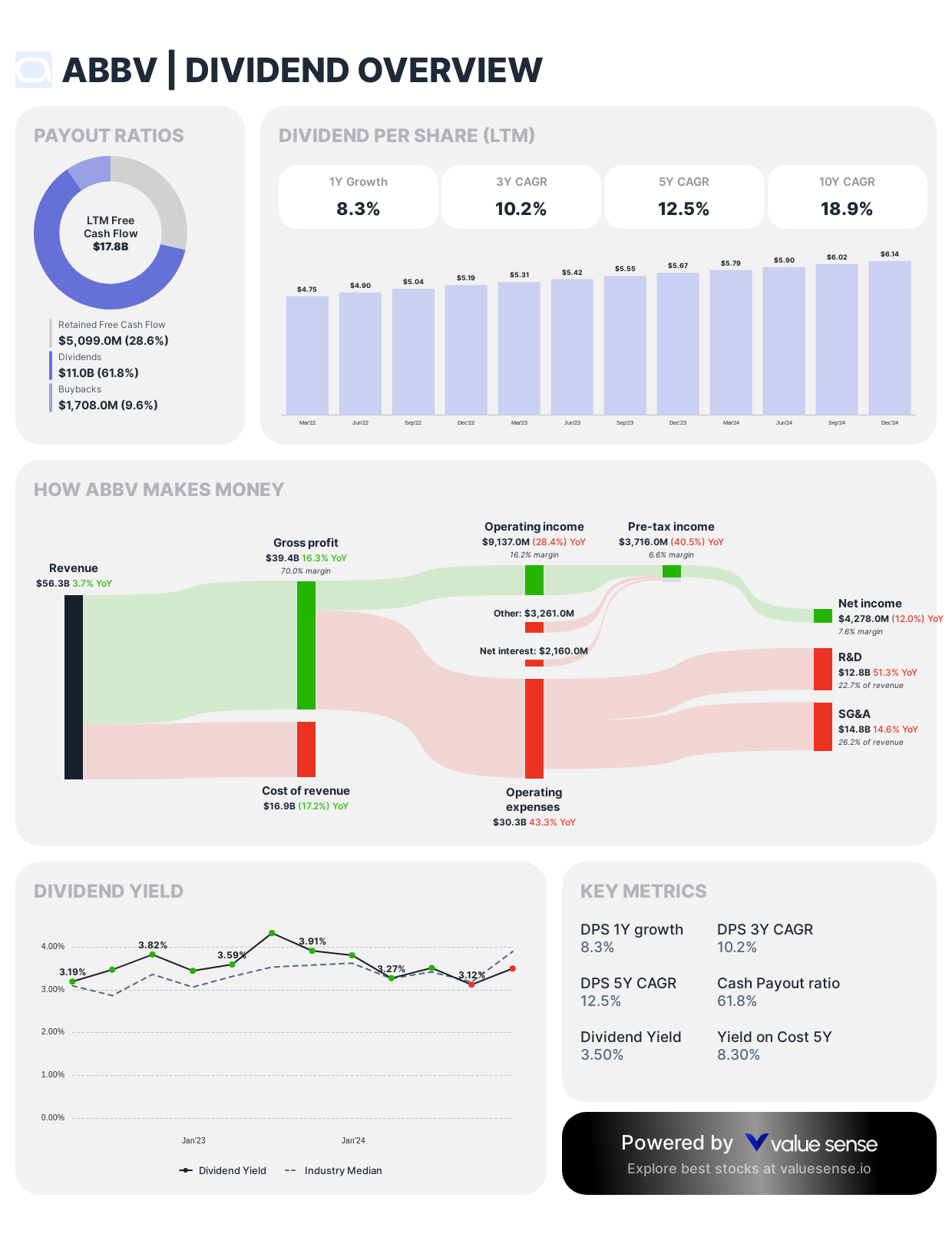
AbbVie (ABBV)
ABBV received multiple mentions as a top dividend pick for 2025, though with less detailed commentary than some other selections.
Dividend Framework: Since its 2013 Abbott Laboratories spin-off, AbbVie has established an accelerated dividend growth trajectory, demonstrating aggressive annual increases despite patent cliff concerns for its flagship Humira medication.
Strategic Considerations:
- Double-digit dividend growth rates in early independence years
- Carefully managed payout ratio (~40-50%) providing buffer for pipeline investments
- Strategic acquisition approach (notably Allergan) partially motivated by dividend sustainability
Investor Implications: AbbVie's dividend policy reflects management's confidence in navigating Humira patent expiration through pipeline diversification and strategic M&A, offering investors growth-oriented income with pharmaceutical sector exposure.
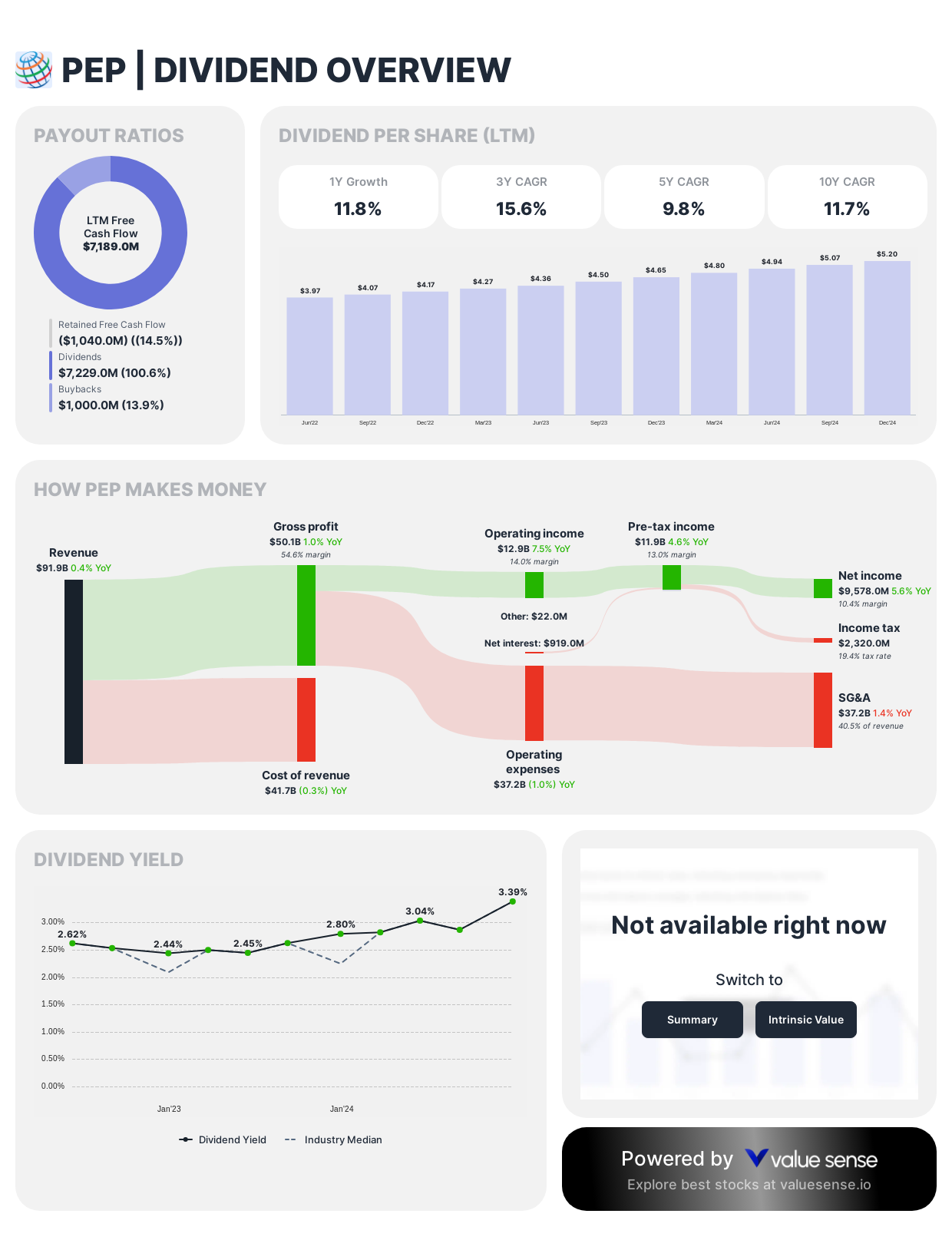
PepsiCo (PEP)
PepsiCo earned mentions for its combination of brand strength and dividend reliability.
Dividend Framework: PepsiCo exhibits a balanced dividend approach characterized by moderate yet highly dependable growth. The company has engineered 50+ consecutive years of dividend increases, reflecting its consistent cash generation across diverse consumer staples categories.
Strategic Considerations:
- Annual dividend increases typically range from 5-7%
- Payout ratio maintained in sustainable 65-70% range
- Complementary share repurchase program enhances total shareholder returns
Investor Implications: PepsiCo's dividend strategy exemplifies disciplined capital allocation, balancing shareholder remuneration with strategic reinvestment in emerging markets and portfolio innovation to drive long-term growth vectors.
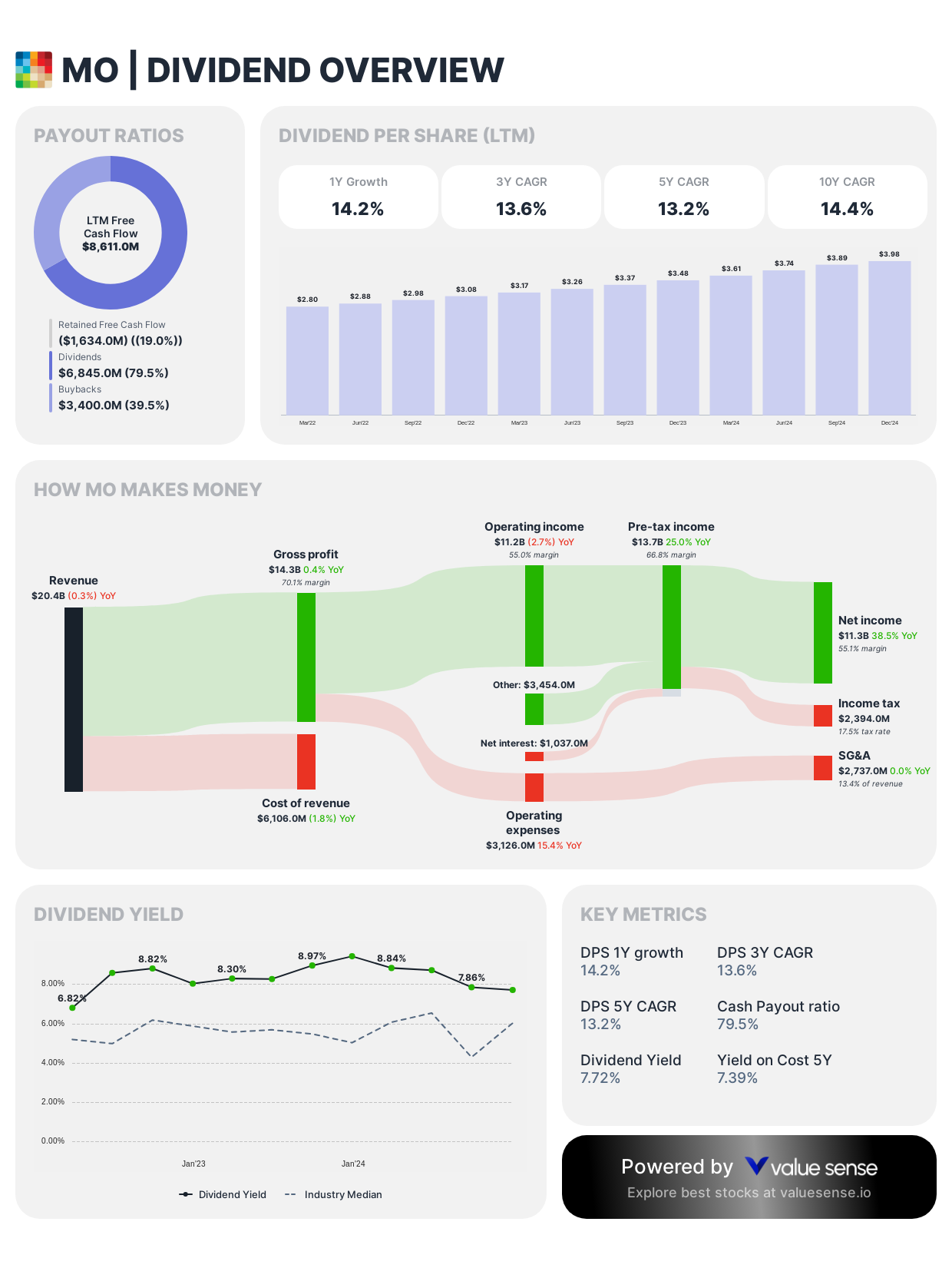
Altria Group (MO)
Altria received endorsements for its very nice dividend, yield and up over 7% YTD, though some investors indicated they avoid tobacco stocks for ethical reasons.
Dividend Framework: Altria maintains one of the market's most robust dividend programs, with a pronounced focus on delivering exceptional shareholder yield. The company's dividend policy features systematic quarterly distributions with consistent annual increases spanning over 50 consecutive years, cementing its position among the elite Dividend Kings.
Strategic Considerations:
- Target payout ratio: 80% of adjusted earnings
- Dividend yield significantly outperforms S&P 500 average (currently ~7-8%)
- Demonstrates dividend resilience despite regulatory headwinds in core tobacco market
Investor Implications: Altria's dividend policy reflects a mature business model generating substantial free cash flow, with management prioritizing income-focused shareholders while balancing strategic investments in reduced-risk products for long-term sustainability.
Conclusion: Diversification Remains Key
For investors looking ahead to 2025, a balanced approach incorporating various dividend-paying sectors - from energy infrastructure and healthcare to consumer staples and REITs - may provide both income stability and potential for capital appreciation in what could be a challenging market environment.
For more investment insights and stock analysis, subscribe to the Value Sense platform.
Explore More Investment Opportunities

For investors seeking undervalued companies with high fundamental quality, our analytics team provides curated stock lists:
📌 50 Undervalued Stocks (Best overall value plays for 2025)
📌 50 Undervalued Dividend Stocks (For income-focused investors)
📌 50 Undervalued Growth Stocks (High-growth potential with strong fundamentals)
🔍 Check out these stocks on the Value Sense platform for free!
More Articles You Might Like
📖 6 High-Potential Micro-Cap Stocks for 2025
📖 Warren Buffett's Investment Evolution: From Graham to Munger
📖 9 Fast-Growing Stocks with Strong Momentum and Undervalued Status
FAQ – Common Questions About High-Momentum Stocks
💡 What exactly are dividends and how do they function within an investment portfolio?
Dividends represent distributed portions of corporate earnings to shareholders, functioning as tangible cash flow mechanisms distinct from price appreciation. These distributions manifest through several structural approaches:
- Cash Dividends: Direct monetary payments, typically distributed quarterly
Portfolio functionality extends beyond simple income generation, creating multi-dimensional investment benefits including reduced volatility (evidenced by historical standard deviation reduction of dividend-paying securities), downside protection through tangible return components, and psychological investment discipline through consistent cash flow visibility.
The critical differentiation between dividends and capital appreciation lies in their fundamental nature—dividends represent actual distributed earnings rather than theoretical market-assigned valuations, creating portfolio stability regardless of prevailing market sentiment fluctuations.
- Stock Dividends: Additional shares proportional to existing ownership
- Special Dividends: Non-recurring distributions following exceptional financial events
- Dividend Reinvestment Programs (DRIPs): Systematic reinvestment structures creating compound growth dynamics
💡 How are dividend yields calculated and what do they reveal about investment opportunities?
Dividend yield calculations utilize a relatively straightforward mathematical framework dividing annual dividend distributions by current share price:
Dividend Yield = (Annual Dividends per Share ÷ Current Share Price) × 100%
For example, a company distributing $2.50 annually trading at $50 per share exhibits a 5% dividend yield.
However, yield interpretation requires nuanced analysis beyond surface-level percentages:
Contextual Factors Affecting Yield Interpretation:
- Market-Driven vs. Distribution-Driven Yields: Elevated yields can reflect either increased distributions (positive) or price deterioration (potentially negative)
- Sector-Specific Yield Expectations: Different industries maintain distinct payout characteristics requiring comparative analysis
- Payout Ratio Correlation: Dividend sustainability requires examination of distribution relative to earnings capacity
- Historical Yield Patterns: Current yields require contextual framing within company-specific yield ranges
- Growth-Adjusted Yield: Forward-looking analysis incorporating projected distribution increases
Yield compression often accompanies dividend growth stocks as price appreciation outpaces distribution increases, creating investor return composition primarily through capital appreciation despite consistent dividend increases.
Excessive yields (typically exceeding 7-8% outside specialized structures) frequently signal market concerns regarding distribution sustainability rather than exceptional value opportunities.
💡 What tax considerations impact dividend investment strategies?
Dividend taxation represents a complex landscape with significant portfolio construction implications across multiple dimensions:
Qualified vs. Ordinary Dividend Classification:
- Qualified dividends receive preferential tax treatment (0%, 15%, or 20% based on income brackets)
- Ordinary dividends face taxation at standard income rates
- Qualification requirements include minimum holding periods and issuing entity characteristics
Account Placement Strategy:
- Tax-advantaged accounts (IRAs, 401(k)s) eliminate immediate dividend taxation
- Taxable accounts create current tax liability but potentially beneficial long-term capital gains treatment
- Strategic placement prioritizes high-yield ordinary dividend securities in tax-advantaged accounts
Specialized Investment Structures:
- Master Limited Partnerships (MLPs) distribute partially tax-deferred income through return of capital mechanisms
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) receive corporate-level tax exemption but distribute primarily ordinary income dividends
- Business Development Companies (BDCs) similarly pass through ordinary income
International Dividend Considerations:
- Foreign withholding taxes potentially create double-taxation scenarios
- Tax treaties establish varying withholding rates by country
- Foreign tax credits potentially offset domestic liability
Tax efficiency metrics extend beyond simple yield analysis, requiring examination of after-tax total return rather than pre-tax distribution percentages, particularly when constructing multi-account investment frameworks.
💡 How does dividend reinvestment impact long-term investment performance?
Dividend reinvestment introduces powerful compounding mechanics with substantial long-term performance implications through several key mechanisms:
Mathematical Compounding Framework:
- Continuously increasing share count generates progressively larger dividend distributions
- Automatic reinvestment removes psychological barriers to consistent investment
- Dollar-cost averaging effects naturally capture price volatility advantages
Empirical Performance Metrics:
- Historical analysis indicates approximately 40% of total S&P 500 returns derived from reinvested dividends since 1940
- Compounding acceleration intensifies with extended time horizons
- Reinvestment during market downturns creates enhanced recovery dynamics
Strategic Reinvestment Approaches:
- Automatic DRIP programs (potentially offering discount mechanisms like OXLC's 5% discount)
- Manual reinvestment allowing selective security allocation
- Hybrid models concentrating distributions during opportunistic market conditions
Psychological Investment Benefits:
- Reduced emotional decision-making through systematic reinvestment
- Heightened focus on income growth rather than price volatility
- Portfolio construction discipline through consistent capital deployment
Performance divergence between reinvestment and income-harvesting approaches increases exponentially with time, creating substantial wealth differentiation over multi-decade horizons despite identical initial investment parameters.
💡 What metrics beyond yield should investors evaluate when constructing dividend portfolios?
Comprehensive dividend analysis requires multi-dimensional evaluation beyond simple yield metrics:
Dividend Growth Metrics:
- 5-year compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of distributions
- Growth consistency patterns (steadiness vs. volatility)
- Management forward guidance regarding distribution policies
Payout Sustainability Analysis:
- Payout ratio relative to earnings (optimal ranges vary by sector)
- Free cash flow coverage ratios providing more accurate sustainability metrics
- Debt service obligations potentially competing with shareholder distributions
Quality Indicators:
- Return on invested capital (ROIC) revealing management capital allocation efficiency
- Competitive positioning within industry landscape
- Margin stability through economic cycles
Financial Structure Evaluation:
- Balance sheet strength supporting distribution continuity during challenging periods
- Capital expenditure requirements potentially constraining future distribution growth
- Regulatory frameworks affecting distribution capabilities (particularly utilities, financial institutions)
Economic Sensitivity Mapping:
- Distribution performance during previous recessions
- Interest rate sensitivity correlation
- Inflation protection characteristics
Dimensional analysis integrating these metrics creates nuanced portfolio construction beyond simplistic yield-chasing approaches, balancing current income against distribution growth potential, quality characteristics, and economic cycle positioning.
Properly constructed dividend portfolios reflect intentional positioning across yield spectrum, growth potential, and quality dimensions rather than concentration within single-factor selection parameters.
