Undervalued Infrastructure Stocks: 5 Economic Recovery Value Plays

Welcome to the Value Sense Blog, your resource for insights on the stock market! At Value Sense, we focus on intrinsic value tools and offer stock ideas with undervalued companies. Dive into our research products and learn more about our unique approach at valuesense.io
Explore diverse stock ideas covering technology, healthcare, and commodities sectors. Our insights are crafted to help investors spot opportunities in undervalued growth stocks, enhancing potential returns. Visit us to see evaluations and in-depth market research.
The infrastructure sector represents one of the most compelling investment opportunities in 2025, combining essential economic function with unprecedented government support and technological transformation. As investors seek undervalued infrastructure stocks 2025 opportunities, a select group of companies trades at significant discounts to intrinsic value while positioning for massive economic recovery benefits.
The Biden Administration's $1.2 trillion Bipartisan Infrastructure Law continues driving historic investments across transportation, energy, and telecommunications infrastructure. Combined with private sector digitalization trends and AI-driven energy demands, the infrastructure landscape presents multiple value creation catalysts that sophisticated investors are beginning to recognize.
This comprehensive analysis examines five exceptional cheap infrastructure stocks trading at substantial discounts to fair value, representing different infrastructure subsectors with unique value propositions and recovery potential. From utility giants managing essential services to technology infrastructure providers enabling digital transformation, these companies offer compelling risk-adjusted returns for patient value investors.
Infrastructure Investment Renaissance: The 2025 Opportunity
Government Spending Catalyst
The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) represents the largest federal infrastructure investment since the Interstate Highway System, allocating $695 billion in announced funding across 74,000+ projects nationwide. This sustained government spending creates predictable revenue streams and growth visibility for infrastructure companies positioned to benefit from modernization initiatives.
Key Investment Areas:
- Transportation Infrastructure: $284 billion for roads, bridges, and public transit systems
- Broadband Expansion: $65 billion for high-speed internet access in underserved areas
- Electric Grid Modernization: $73 billion for power grid resilience and clean energy transmission
- Water Systems: $55 billion for drinking water and wastewater infrastructure improvements
Private Sector Digitalization
Beyond government investments, private sector digitalization drives unprecedented demand for technology infrastructure. AI workload acceleration, cloud computing expansion, and 5G network deployment create sustained growth opportunities for infrastructure providers across multiple subsectors.
Digital Infrastructure Drivers:
- Data Center Demand: AI and cloud computing require massive computational infrastructure
- 5G Network Rollout: Telecommunications infrastructure expansion enables next-generation connectivity
- Smart Grid Technology: Utility infrastructure modernization improves efficiency and reliability
- Industrial Automation: Manufacturing and logistics digitization demands robust infrastructure platforms
The Five Value Opportunities
1. Pacific Gas & Electric (PCG): Utility Transformation Value Play
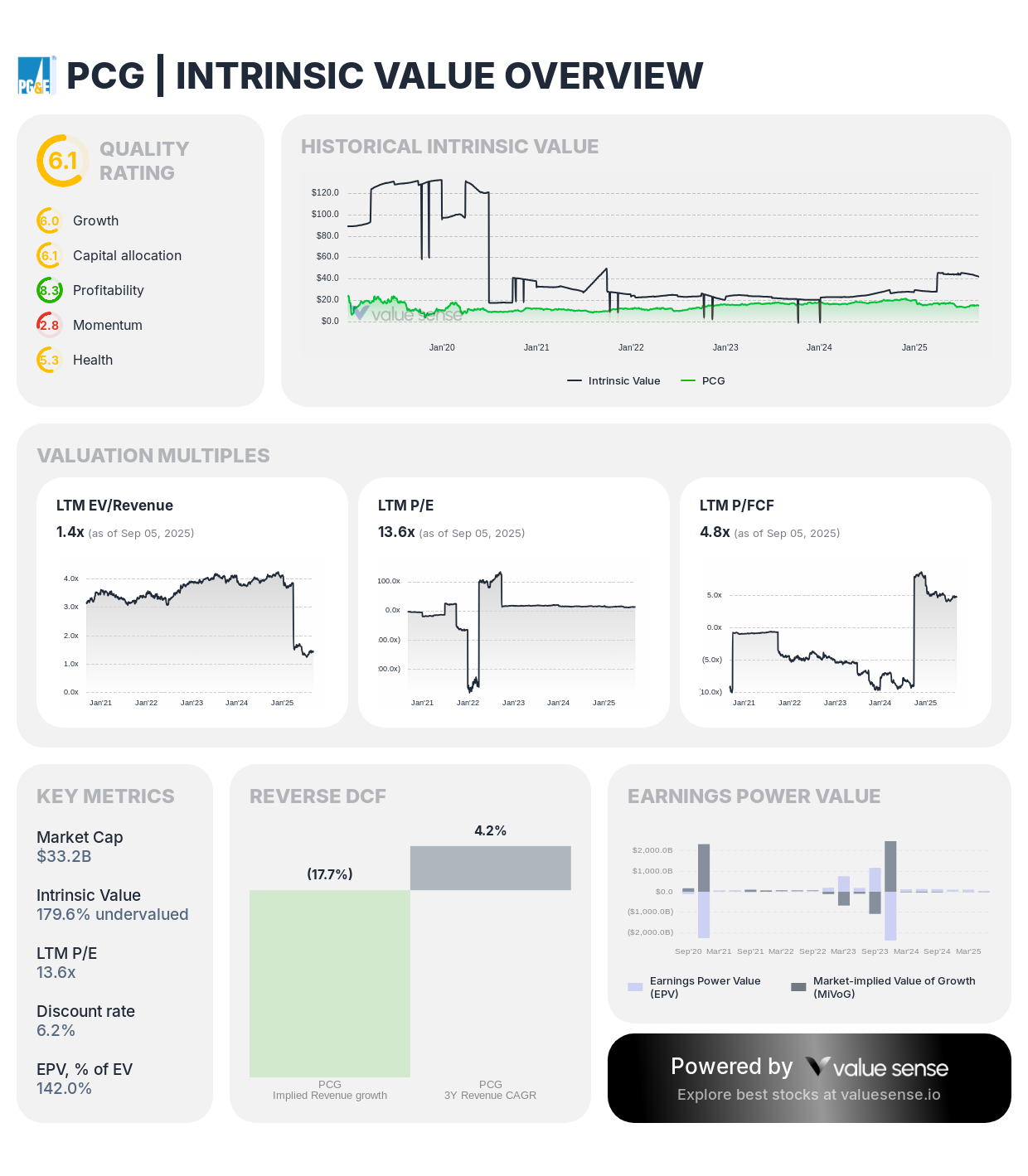
PCG demonstrates exceptional undervaluation at 179.6% below intrinsic value with strong cash generation and quality improvements
Company Profile: Pacific Gas & Electric operates as California's largest utility, serving 16 million customers across Northern and Central California through gas and electric distribution networks.
Value Proposition:
- Extreme Undervaluation: 179.6% undervalued relative to intrinsic value
- Quality Rating: 6.1/10 with improving operational metrics
- Market Cap: $33.2 billion with substantial recovery potential
- Cash Generation: $6.93 billion free cash flow with 28.3% FCF margin
Investment Thesis: PCG represents the most undervalued opportunity among infrastructure stocks, trading at a massive discount following bankruptcy resolution and operational improvements. The company's essential utility services, regulatory recovery mechanisms, and wildfire mitigation investments position it for sustained value creation.
Key Catalysts:
- Wildfire Risk Reduction: Comprehensive mitigation programs reduce liability exposure
- Rate Base Growth: Infrastructure investments generate regulated returns
- Clean Energy Transition: California's decarbonization creates growth opportunities
- Operational Excellence: Post-bankruptcy focus improves safety and reliability
Financial Strength:
- Revenue Growth: 1.3% with stability from regulated operations
- ROIC: 9.3% demonstrating effective capital allocation
- Free Cash Flow: Exceptional 28.3% margin supports dividend restoration potential
- Balance Sheet: Post-bankruptcy capital structure provides financial flexibility
2. Enbridge (ENB): Energy Infrastructure Backbone
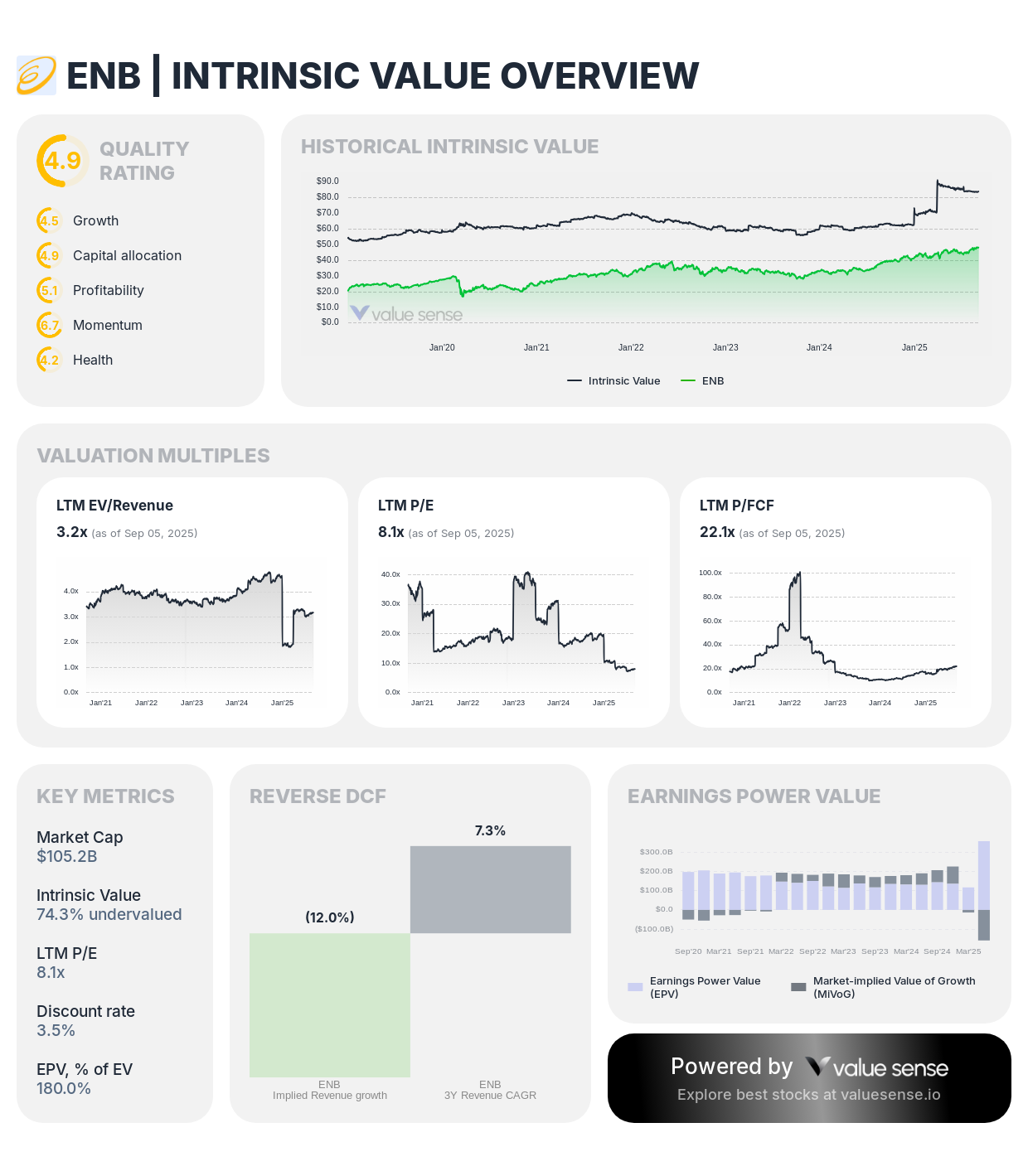
Enbridge shows 74.3% undervaluation with exceptional revenue growth and stable cash flows from diversified energy infrastructure
Company Profile: Enbridge operates North America's largest energy infrastructure network, including oil pipelines, natural gas distribution, and renewable power generation across the continent.
Value Proposition:
- Significant Undervaluation: 74.3% discount to intrinsic value
- Quality Rating: 4.9/10 with strong fundamental characteristics
- Market Cap: $105.2 billion reflecting substantial scale
- Revenue Growth: Exceptional 48.5% driven by asset expansion
Investment Thesis: ENB provides essential energy transportation and distribution services with regulated utility-like characteristics. The company's diversified energy infrastructure portfolio generates predictable cash flows while participating in North America's energy transition through renewable investments and natural gas expansion.
Key Catalysts:
- Pipeline Network Expansion: Strategic acquisitions and organic growth projects
- Natural Gas Demand: Increasing demand from power generation and industrial users
- Renewable Energy Growth: Wind and solar development complements traditional assets
- Dividend Aristocrat: 29-year dividend growth streak demonstrates cash flow reliability
Financial Excellence:
- Revenue Scale: $14.9 billion with diversified revenue streams
- Cash Generation: $4.76 billion free cash flow with 7.4% margin
- ROIC: 6.7% on substantial asset base
- Dividend Yield: Attractive income with sustainable payout coverage
3. CommScope (COMM): Telecommunications Infrastructure Recovery
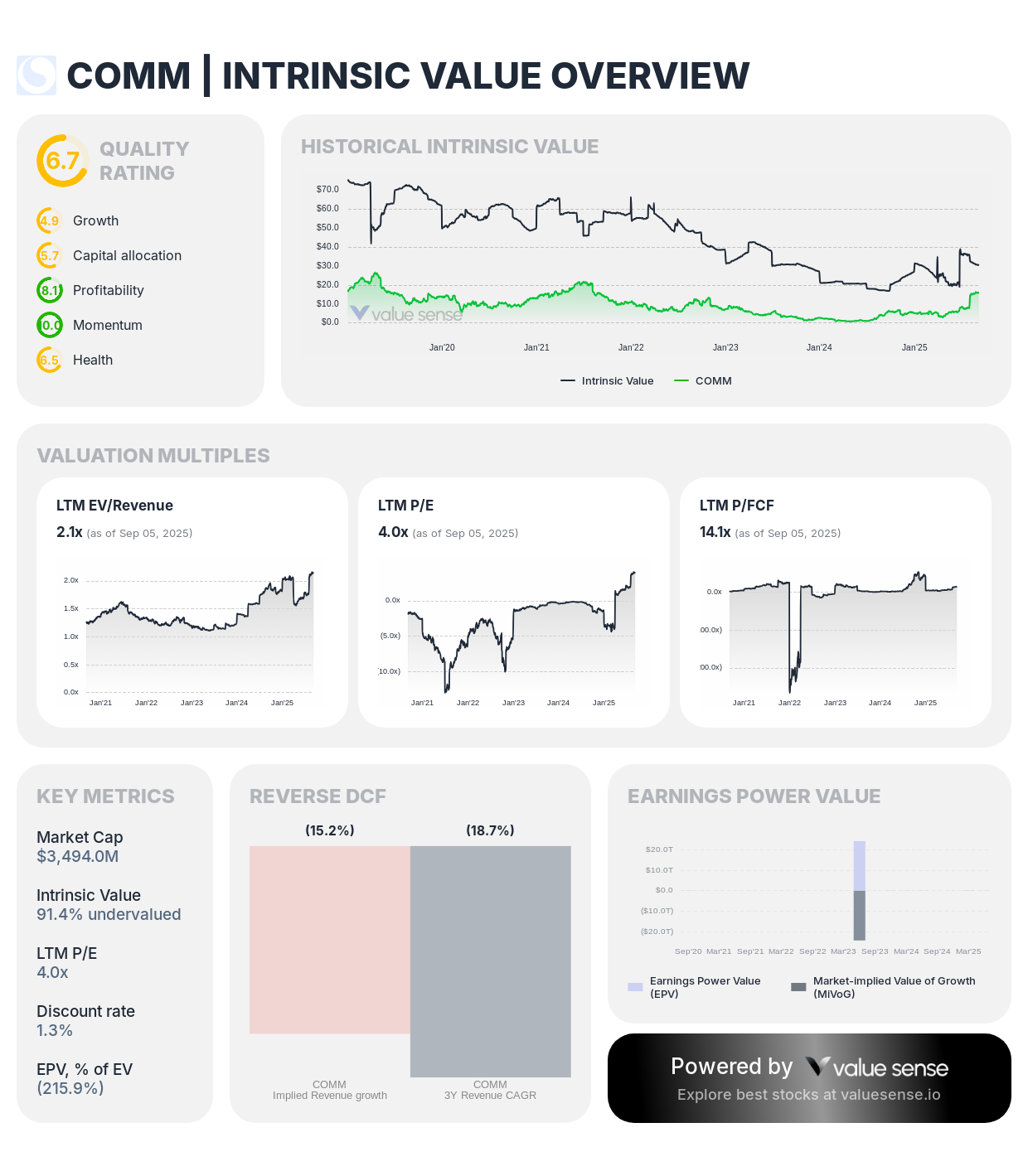
CommScope trades at 91.4% undervaluation with highest quality rating and positioning for 5G infrastructure buildout recovery
Company Profile: CommScope designs and manufactures infrastructure solutions for communications networks, including wireless, broadband, and enterprise connectivity technologies.
Value Proposition:
- Deep Undervaluation: 91.4% below intrinsic value
- Highest Quality Rating: 6.7/10 among analyzed companies
- Market Cap: $3.49 billion representing recovery opportunity
- Revenue Growth: Strong 11.0% expansion
Investment Thesis: COMM represents a classic value recovery play in telecommunications infrastructure. The company's leading position in network equipment and services positions it to benefit from 5G rollout acceleration, broadband expansion initiatives, and enterprise connectivity upgrades.
Key Catalysts:
- 5G Network Deployment: Accelerating infrastructure investments drive equipment demand
- Broadband Infrastructure Act: Government funding supports rural connectivity expansion
- Enterprise Digitalization: Corporate network upgrades create sustained demand
- Operational Turnaround: Management focuses on profitability improvement and debt reduction
Operational Metrics:
- Revenue: $1.39 billion with improving mix
- Free Cash Flow: $248 million with 5.2% margin
- ROIC: 4.7% with improvement potential
- Balance Sheet: Debt reduction priorities support financial stability
4. Otis Worldwide (OTIS): Vertical Transportation Infrastructure
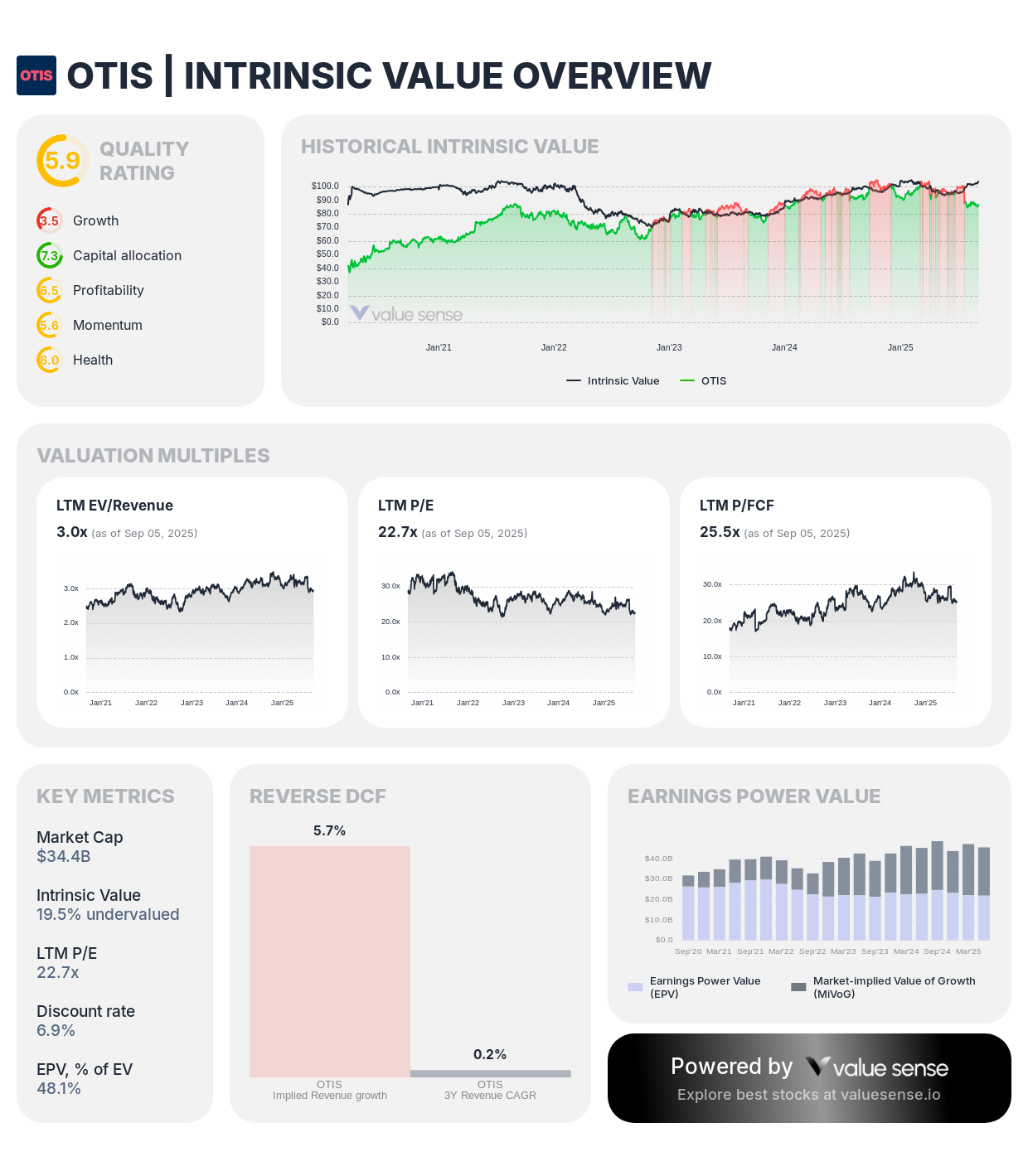
Otis demonstrates 19.5% undervaluation with exceptional 27.1% ROIC and stable service revenue model
Company Profile: Otis Worldwide manufactures, installs, and services elevators and escalators globally, serving residential, commercial, and infrastructure markets worldwide.
Value Proposition:
- Conservative Undervaluation: 19.5% discount to fair value
- Quality Rating: 5.9/10 with strong business characteristics
- Market Cap: $34.4 billion in established market leader
- Exceptional ROIC: 27.1% demonstrates capital efficiency
Investment Thesis: OTIS operates a unique infrastructure business model combining equipment manufacturing with high-margin maintenance services. Urban development trends, building modernization needs, and infrastructure investments drive sustained demand for vertical transportation solutions.
Key Catalysts:
- Urbanization Trends: Global urban population growth drives elevator demand
- Building Modernization: Aging infrastructure requires upgrades and replacements
- Service Revenue Growth: Recurring maintenance contracts provide predictable cash flows
- Technology Integration: Smart building systems create premium service opportunities
Financial Quality:
- Service Revenue: $3.96 billion from maintenance contracts
- Cash Generation: $1.35 billion free cash flow with 9.5% margin
- Capital Efficiency: Industry-leading 27.1% ROIC
- Revenue Stability: Flat 0.1% growth reflects market maturity but stable demand
5. Nucor Corporation (NUE): Steel Infrastructure Foundation
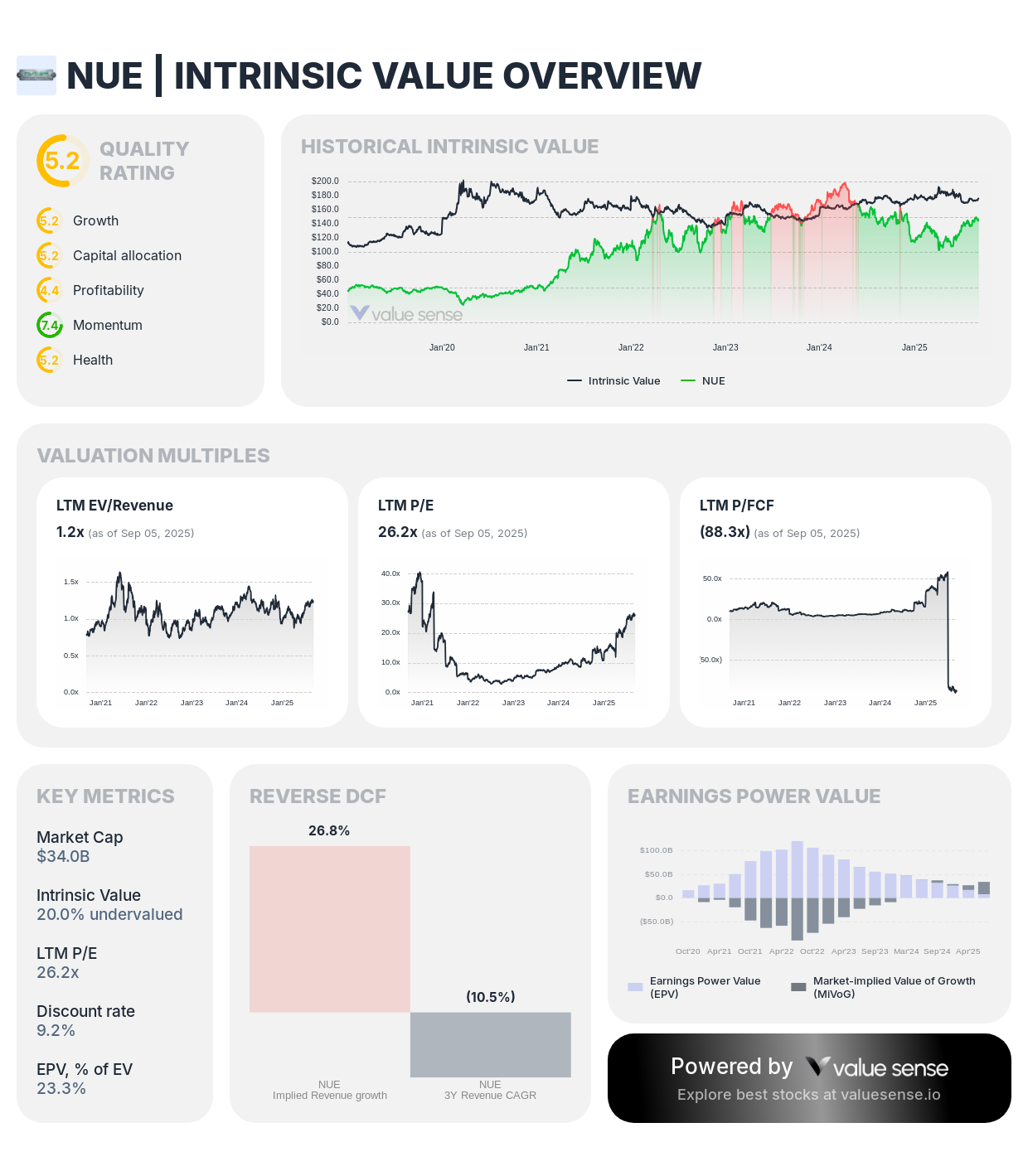
Nucor shows 20.0% undervaluation with steady revenue growth and positioning for infrastructure construction demand
Company Profile: Nucor operates as North America's largest steel producer and recycler, manufacturing steel products for construction, automotive, and industrial applications.
Value Proposition:
- Modest Undervaluation: 20.0% below intrinsic value
- Quality Rating: 5.2/10 with cyclical business characteristics
- Market Cap: $34.0 billion in leading steel producer
- Revenue Growth: Steady 5.8% expansion
Investment Thesis: NUE provides essential steel products for infrastructure construction while maintaining cost advantages through electric arc furnace technology and scrap steel recycling. Infrastructure spending acceleration and nearshoring trends support sustained steel demand.
Key Catalysts:
- Infrastructure Construction: Government spending drives steel demand for bridges, buildings, and transportation
- Manufacturing Reshoring: Domestic production trends favor North American steel suppliers
- Technology Advantages: Electric arc furnaces provide cost and environmental benefits
- Market Leadership: Dominant position enables pricing power and market share maintenance
Operational Considerations:
- Revenue: Strong growth from infrastructure and construction demand
- Cyclical Nature: Steel pricing volatility affects profitability
- Environmental Benefits: Recycling capabilities align with sustainability trends
- Capital Allocation: Disciplined investment approach maintains competitive advantages
Sector Analysis and Investment Themes
Utilities Infrastructure Modernization
The utility sector presents exceptional value opportunities as companies invest in grid modernization, renewable energy integration, and resilience improvements. Regulatory frameworks provide visibility for capital recovery while climate initiatives drive growth investments.
Investment Drivers:
- Grid Modernization: Smart grid technology improves efficiency and reliability
- Renewable Integration: Clean energy transition requires substantial infrastructure investment
- Climate Resilience: Extreme weather events drive infrastructure hardening investments
- Electric Vehicle Adoption: Transportation electrification increases electricity demand
Telecommunications Infrastructure Expansion
5G network deployment and broadband expansion create sustained growth opportunities for telecom infrastructure providers. Government initiatives and private sector digitalization drive unprecedented connectivity investments.
Growth Catalysts:
- 5G Network Rollout: Wireless carriers invest billions in network infrastructure
- Rural Broadband: Federal funding supports connectivity expansion
- Enterprise Networking: Corporate digital transformation drives equipment demand
- Edge Computing: Distributed computing requires expanded network infrastructure
Transportation Infrastructure Investment
Transportation infrastructure modernization encompasses roads, bridges, airports, and public transit systems. Bipartisan Infrastructure Law funding provides multi-year visibility for construction and engineering companies.
Market Opportunities:
- Bridge Replacement: Aging infrastructure requires substantial investment
- Airport Modernization: Travel recovery drives terminal and runway improvements
- Public Transit: Electric buses and rail systems receive federal support
- Freight Networks: E-commerce growth demands logistics infrastructure expansion
Financial Comparison Analysis
| Company | Market Cap | Undervaluation | Quality Rating | Revenue Growth | ROIC | FCF Margin | Key Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCG | $33.2B | 179.6% | 6.1 | 1.3% | 9.3% | 28.3% | Extreme value, utility stability |
| ENB | $105.2B | 74.3% | 4.9 | 48.5% | 6.7% | 7.4% | Energy infrastructure scale |
| COMM | $3.49B | 91.4% | 6.7 | 11.0% | 4.7% | 5.2% | 5G infrastructure growth |
| OTIS | $34.4B | 19.5% | 5.9 | 0.1% | 27.1% | 9.5% | Service model stability |
| NUE | $34.0B | 20.0% | 5.2 | 5.8% | 1.9% | -1.2% | Steel infrastructure demand |
Risk Analysis and Mitigation Strategies
Regulatory and Political Risks
Infrastructure companies face regulatory oversight and political influence affecting operations, pricing, and investment recovery. Changes in government priorities or regulatory frameworks can impact profitability and growth prospects.
Mitigation Approaches:
- Diversified Geographic Exposure: Multi-jurisdictional operations reduce single-market risk
- Regulatory Engagement: Active participation in policy development processes
- Essential Service Provision: Critical infrastructure status provides political protection
- Stakeholder Alignment: Community and customer relationships support favorable treatment
Economic Cycle Sensitivity
Infrastructure investments often correlate with economic cycles, affecting demand, pricing, and project timing. Economic downturns can delay projects and reduce infrastructure utilization.
Risk Management:
- Regulated Revenue Streams: Utility-style cash flows provide cycle protection
- Essential Infrastructure: Critical services maintain demand during downturns
- Government Backing: Public sector support provides counter-cyclical stability
- Long-Term Contracts: Multi-year agreements reduce short-term volatility
Technology Disruption Risks
Technological advancement can disrupt traditional infrastructure business models, requiring adaptation and investment to maintain competitive positioning.
Adaptation Strategies:
- Innovation Investment: R&D spending ensures technological leadership
- Partnership Development: Strategic alliances access emerging technologies
- Business Model Evolution: Service expansion beyond traditional infrastructure
- Digital Integration: Technology adoption improves operational efficiency
Investment Strategy Recommendations
Value Investor Approach
Portfolio Allocation Strategy:
- Core Holdings (40-50%): PCG and ENB for deep value and cash flow stability
- Growth Positions (30-35%): COMM for 5G infrastructure recovery potential
- Diversification Stakes (15-25%): OTIS and NUE for sector balance and cyclical exposure
Entry Timing:
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: Systematic accumulation during market volatility
- Valuation-Based Buying: Increased allocation during further price weakness
- Catalyst-Driven Positions: Accelerated buying ahead of major infrastructure announcements
Growth-Oriented Investment
Technology Infrastructure Focus:
- Primary Emphasis: COMM and telecommunications infrastructure growth
- Supporting Positions: Utility modernization through PCG exposure
- Sector Rotation: Opportunistic moves between subsectors based on momentum
Income-Focused Strategy
Dividend and Cash Flow Priority:
- ENB Core Position: Dividend aristocrat with 29-year growth streak
- PCG Recovery Play: Dividend restoration potential from strong cash flows
- OTIS Stability: Reliable service revenue supports consistent payments
Economic Recovery Positioning
Infrastructure as Economic Multiplier
Infrastructure investments generate significant economic multiplier effects, creating jobs, improving productivity, and enabling economic growth. Companies positioned in this ecosystem benefit from sustained government and private sector spending.
Multiplier Benefits:
- Direct Employment: Construction and maintenance jobs
- Indirect Benefits: Supply chain and service provider demand
- Productivity Improvements: Better infrastructure enables economic efficiency
- Innovation Catalyst: Modern infrastructure supports technological advancement
Long-Term Secular Trends
Demographic and Technology Drivers:
- Population Growth: Urban expansion drives infrastructure demand
- Aging Infrastructure: Replacement cycle creates sustained investment needs
- Climate Adaptation: Resilience requirements drive modernization
- Digital Transformation: Technology infrastructure becomes essential utility
The Investment Verdict
The undervalued infrastructure stocks 2025 opportunity represents a convergence of compelling valuation discounts with unprecedented infrastructure investment drivers. Government spending commitments, private sector digitalization, and demographic trends create multiple catalysts for sustained value creation.
Compelling Investment Case
Value Opportunity: Companies trading at 20-180% discounts to intrinsic value provide exceptional risk-adjusted return potential for patient investors willing to hold through economic cycles.
Government Support: $1.2 trillion in infrastructure spending provides multi-year visibility and growth catalysts that the market hasn't fully recognized in current valuations.
Essential Services: Infrastructure companies provide critical services with defensive characteristics and pricing power that protect against economic uncertainty.
Technology Transformation: Digitalization trends create new growth avenues beyond traditional infrastructure markets, expanding addressable opportunities.
Strategic Recommendation
Strong Buy recommendation for diversified infrastructure portfolio with emphasis on:
- Maximum Value: PCG for extreme undervaluation with recovery potential
- Quality Growth: ENB for scale, diversification, and dividend reliability
- Technology Exposure: COMM for 5G infrastructure acceleration
- Stability Factor: OTIS for defensive characteristics and cash generation
- Economic Recovery: NUE for infrastructure construction demand
The combination of deep value opportunities, government spending catalysts, and long-term secular trends makes infrastructure stocks essential components of 2025 investment portfolios focused on construction value investing and economic recovery positioning.
Explore More Investment Opportunities

For investors seeking undervalued companies with high fundamental quality, our analytics team provides curated stock lists:
📌 50 Undervalued Stocks (Best overall value plays for 2025)
📌 50 Undervalued Dividend Stocks (For income-focused investors)
📌 50 Undervalued Growth Stocks (High-growth potential with strong fundamentals)
🔍 Check out these stocks on the Value Sense platform for free!
More Articles You Might Like
📖 Mastercard Undervalued: Payment Processing Profit Machine
📖 Undervalued Cloud Computing Stocks September 2025
FAQ - Undervalued Infrastructure Stocks
Q: Why are infrastructure stocks undervalued in 2025 despite massive government spending commitments?
A: Infrastructure stocks remain undervalued due to several factors: market focus on AI and technology sectors, concerns about interest rate sensitivity, regulatory uncertainty, and the long-term nature of infrastructure projects. The $1.2 trillion Bipartisan Infrastructure Law benefits haven't fully materialized in stock prices, creating opportunities for patient investors. Companies like PCG (179.6% undervalued) and ENB (74.3% undervalued) demonstrate this disconnect between fundamental value and market pricing.
Q: Which infrastructure subsector offers the best risk-adjusted returns in 2025?
A: Utilities and energy infrastructure offer the best risk-adjusted returns due to regulated revenue streams, essential service characteristics, and government support for modernization. ENB's diversified energy infrastructure and PCG's utility operations provide defensive cash flows while participating in growth trends. Telecommunications infrastructure through COMM offers higher growth potential but with increased volatility from technology cycles.
Q: How does the Biden Infrastructure Bill specifically benefit these companies?
A: The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act provides direct benefits through increased government spending on projects these companies serve. PCG benefits from electric grid modernization funding, ENB from energy infrastructure investments, COMM from broadband expansion initiatives, OTIS from building and transportation infrastructure projects, and NUE from construction material demand. The $695 billion in announced funding creates multi-year revenue visibility.
Q: What are the main risks when investing in undervalued infrastructure stocks?
A: Key risks include regulatory changes affecting utility pricing and project approvals, economic cycles impacting construction and industrial demand, technology disruption requiring capital investment, and interest rate sensitivity affecting infrastructure valuations. However, these companies' essential service nature, government support, and long-term contracts provide significant risk mitigation compared to other sectors.
Q: How should investors position their portfolio allocation among these infrastructure opportunities?
A: A balanced approach would emphasize PCG and ENB (40-50% combined) for deep value and cash flow stability, COMM (20-25%) for growth exposure to 5G infrastructure, and smaller positions in OTIS and NUE (25-35% combined) for diversification and cyclical exposure. Dollar-cost averaging during market volatility optimizes entry timing, while maintaining 3-5 year investment horizons allows infrastructure investment cycles to materialize fully.
