The Importance of Valuation in Growth Stocks: A Value Investing Perspective

In the dynamic world of stock investing, valuation is often the anchor that helps investors avoid the turbulent waters of market speculation. For many, the allure of growth stocks — like Tesla and Palantir — has been irresistible, driven by explosive price rises and retail hype. However, as experienced value investors like the Value Sense analytics team emphasize, true investment success lies in understanding a stock's intrinsic value rather than merely chasing market trends.
Growth Stocks and the Valuation Trap
The Hype Behind Growth Stocks
Over the past few years, growth stocks have dominated headlines and captivated retail investors. Publicly traded company like Tesla, with their innovative products and charismatic leadership, became market darlings, experiencing meteoric rises in their stock prices. New investors flooded into these stocks, often ignoring traditional valuation methods, leading to a market environment heavily influenced by sentiment and momentum.
However, the excitement surrounding these stocks often leads to overvaluation, a dangerous trap for investors. These stocks can skyrocket based on future potential estimates rather than current fundamentals, creating a situation where prices are driven more by hype than by the company's true financial health.
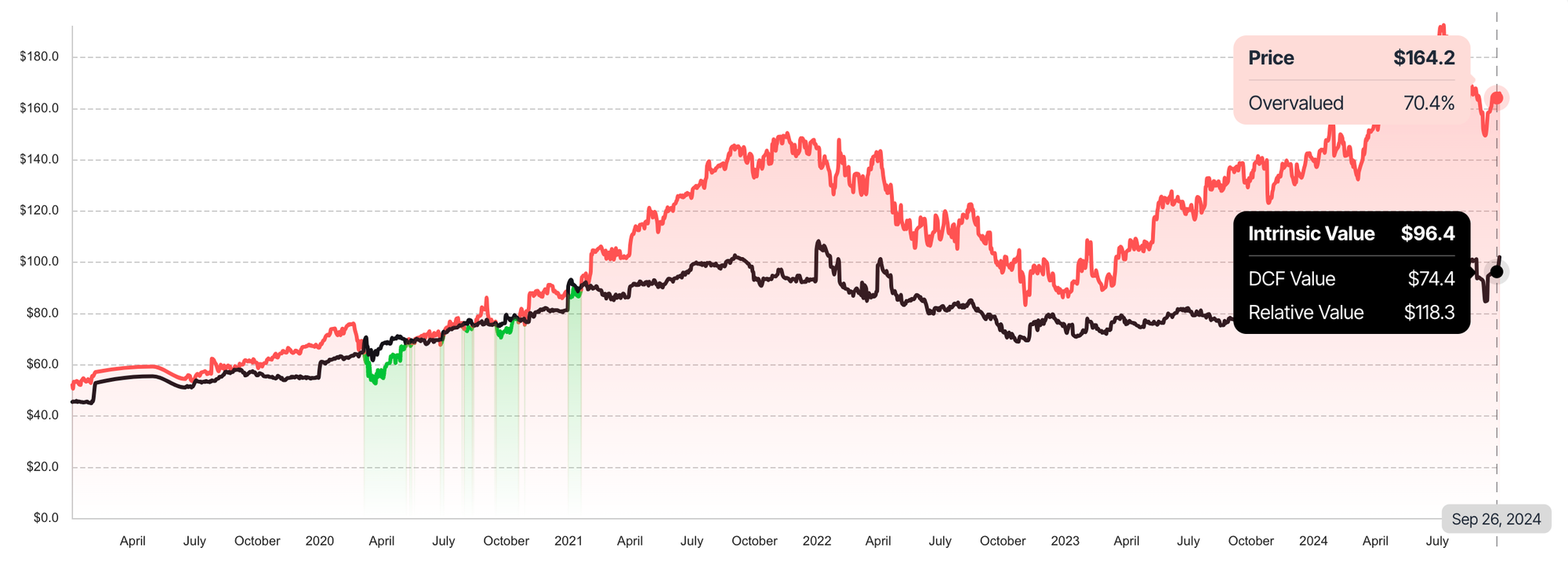
Overvaluation Risk
The core issue with growth stocks is that they can become significantly overvalued during periods of market euphoria. In the case of Tesla, for example, its Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio reached levels far beyond those of its industry peers. This overvaluation poses a risk to investors because, at some point, the market will correct, and prices will realign with the company's fair market value.
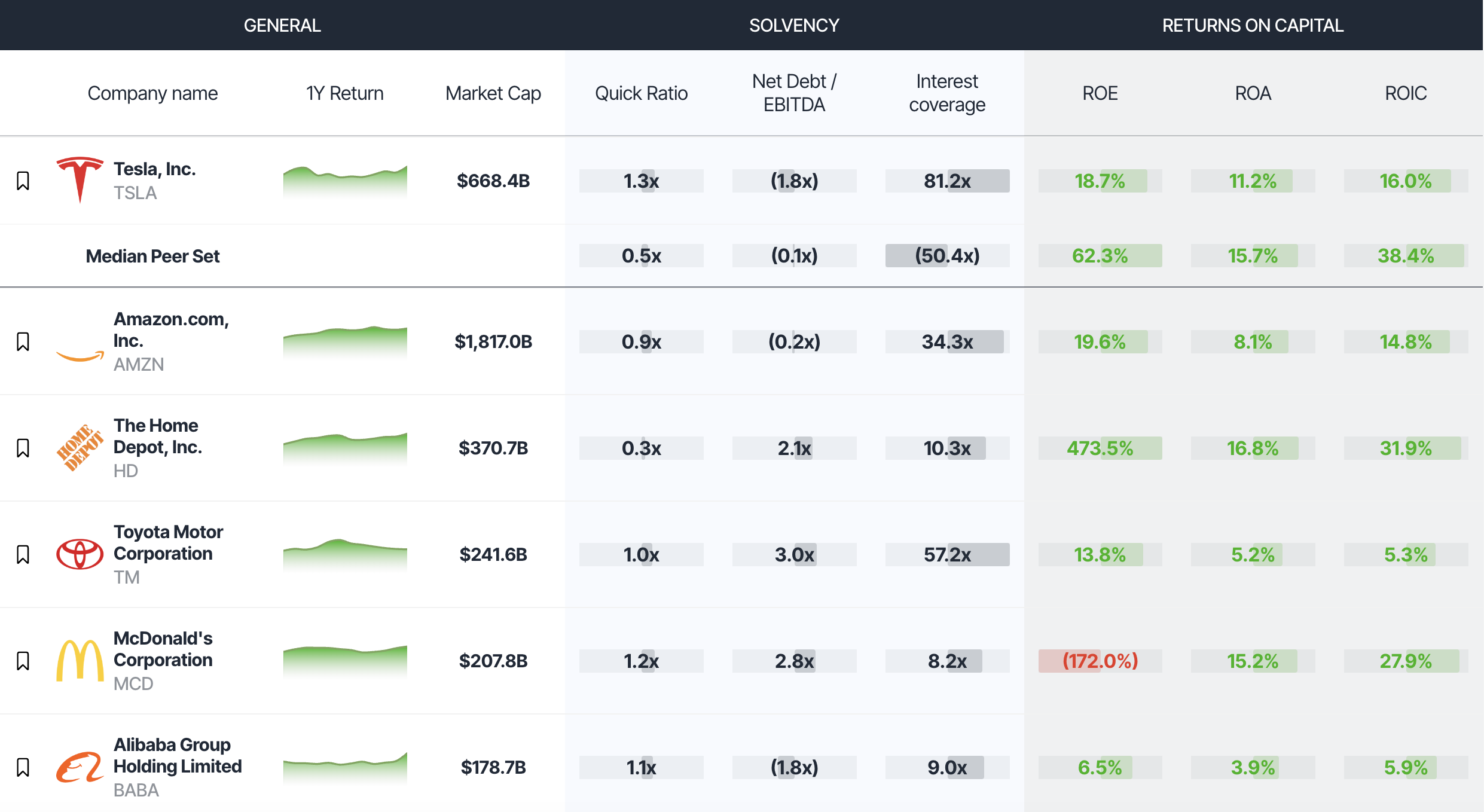
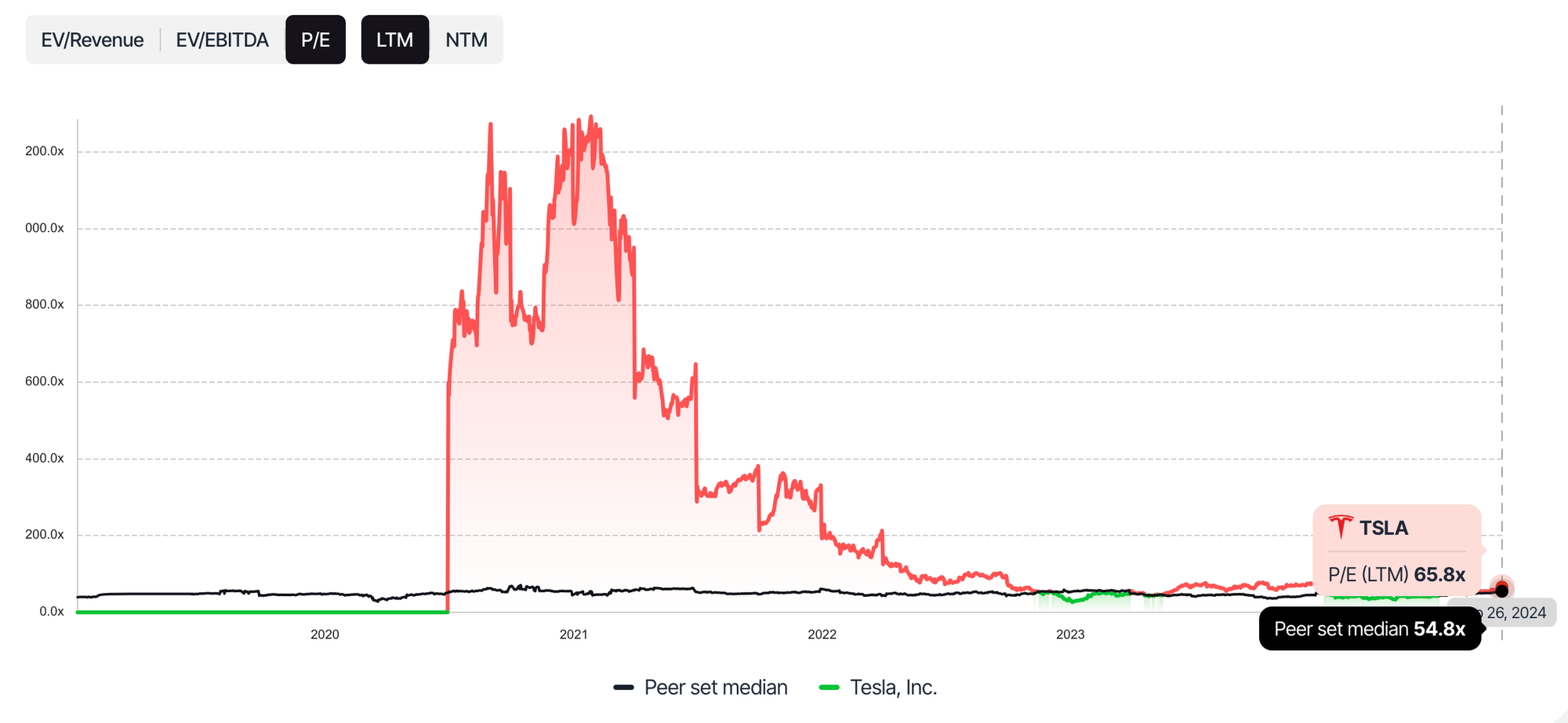
When inexperienced investors, like "your neighbor’s 17-year-old pimply virgin kid," begin hyping these stocks, it’s a sign that the market is driven more by speculation than solid analysis. This "valuation trap" can lead to significant losses when the bubble bursts and prices fall.
Signs of Overvaluation
There are several key indicators of overvaluation that investors should watch for when researching growth stocks:
- Sky-high P/E Ratios: A significantly high P/E ratio compared to industry averages suggests that a stock may be overpriced relative to its earnings.
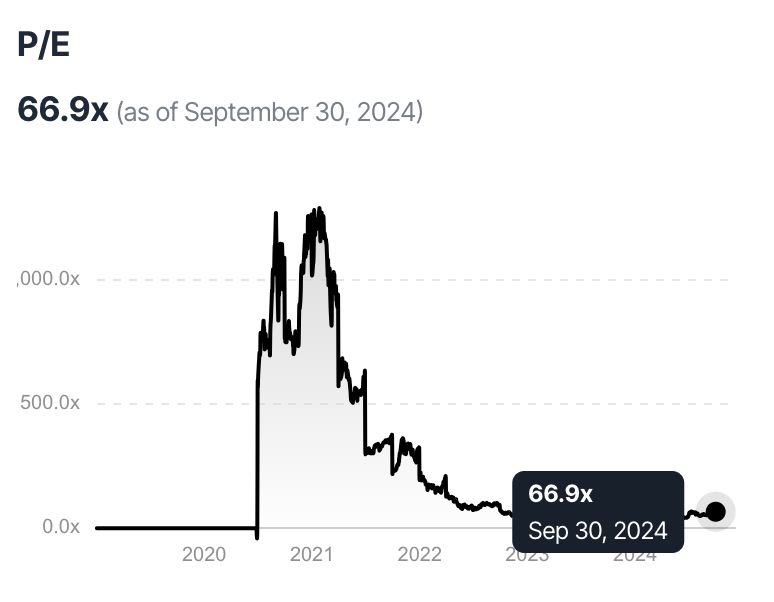
- Over-reliance on future growth: Stocks trading at prices that assume constant high growth rates for many years can be overvalued if those estimates are not met.
- Speculative behavior: When stock prices rise rapidly based on news or hype, without corresponding improvements in fundamentals, it’s often a red flag.
Why Value Investing Prevails
The Fundamentals of Value Investing
Despite the appeal of growth stocks, value investing remains a time-tested approach to building long-term wealth. Value investing focuses on buying companies that are trading below their fair market value based on fundamentals like earnings, revenue, and cash flow. The idea is simple: buy solid companies at a discount and wait for the market to recognize their fair value.
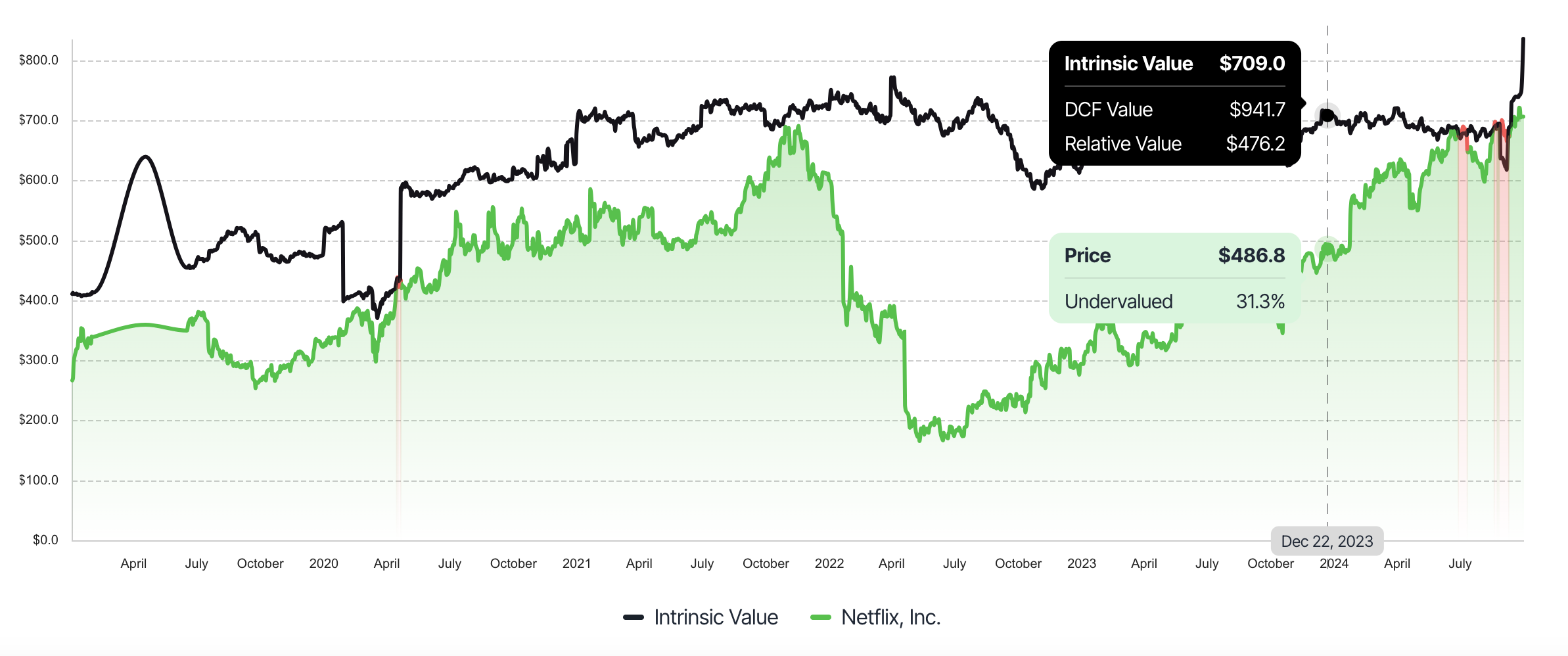
While growth stocks may experience temporary price spikes, business valuation will always "matter with a vengeance." Eventually, stocks must be priced according to their actual financial health, not just future potential.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Thinking
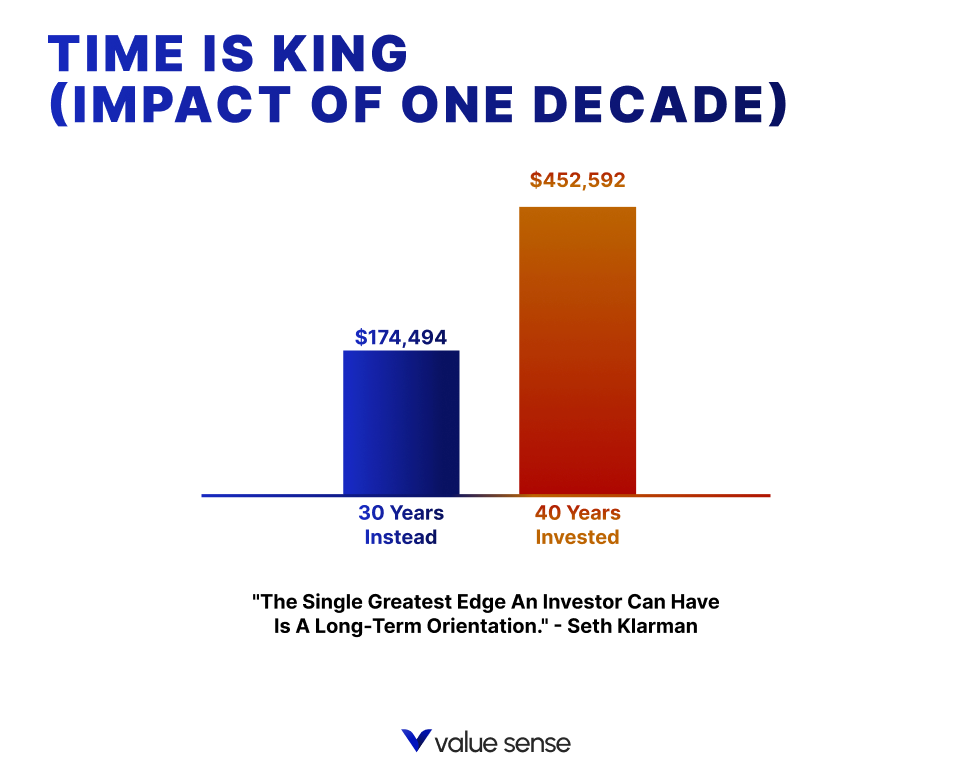
One of the biggest differentiators between value and growth investing is the mindset. Value investing is about long-term thinking, whereas many growth stock investors chase short-term gains. This difference in philosophy can lead to vastly different outcomes. Stocks like Tesla may soar in the short term, but value investors focus on the company's ability to generate profits consistently over many years.
The Voting and Weighing Machine Analogy
As Paul often notes, quoting the legendary investor Ben Graham, "In the short run, the stock market is a voting machine, but in the long run, it’s a weighing machine." This analogy reflects the idea that, in the short term, stock prices may fluctuate based on popularity, but in the long term, a company's true value will be revealed by its performance.
The Role of Psychology in Investing
Emotional Investing Pitfalls
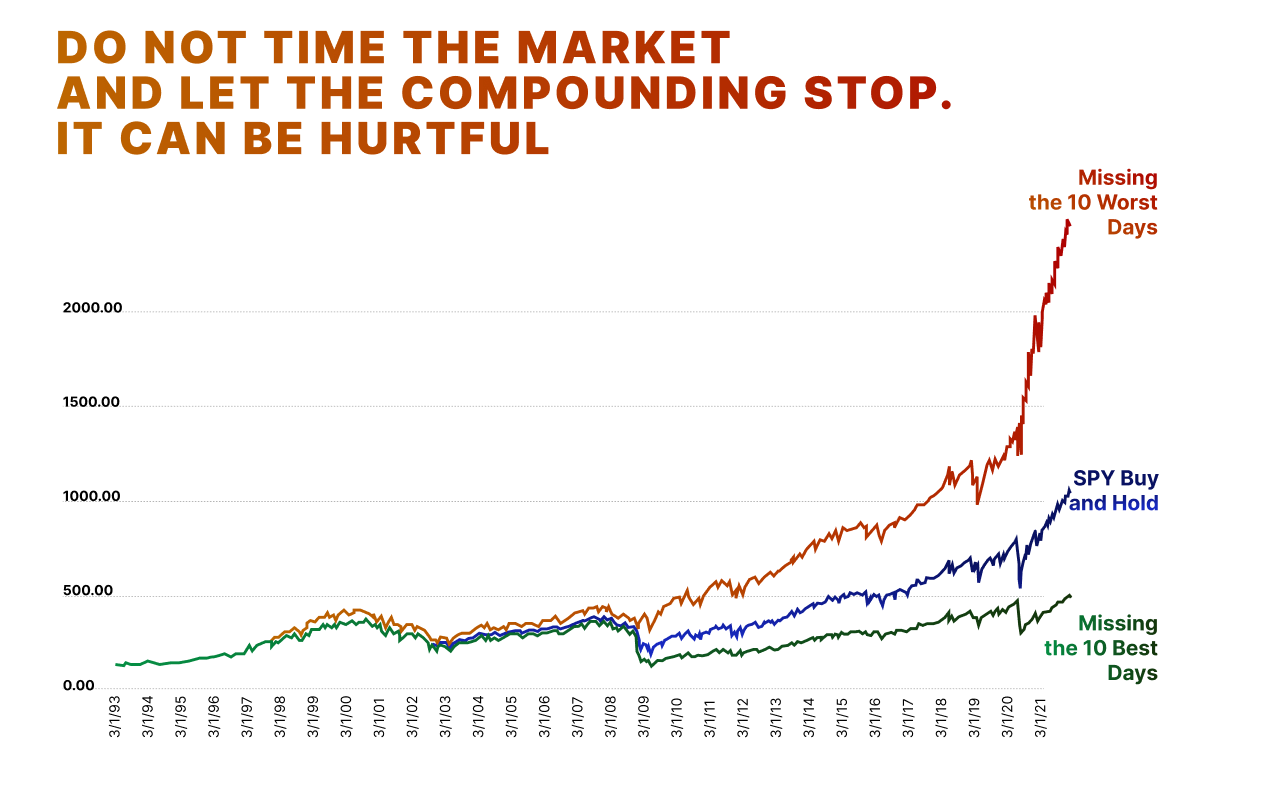
The psychological aspect of investing is often underestimated. While the numbers involved in valuation are straightforward, controlling your emotions is far more challenging. Emotional investing — buying or selling based on fear, excitement, or panic sell — often leads to poor decisions.
For example, when stocks like Palantir begin to fall after a period of rapid growth, many investors panic and sell, even if the company’s fundamentals remain solid. Value investors, however, see this as an opportunity to buy more shares at a discount.
Value Investing as a Psychological Discipline
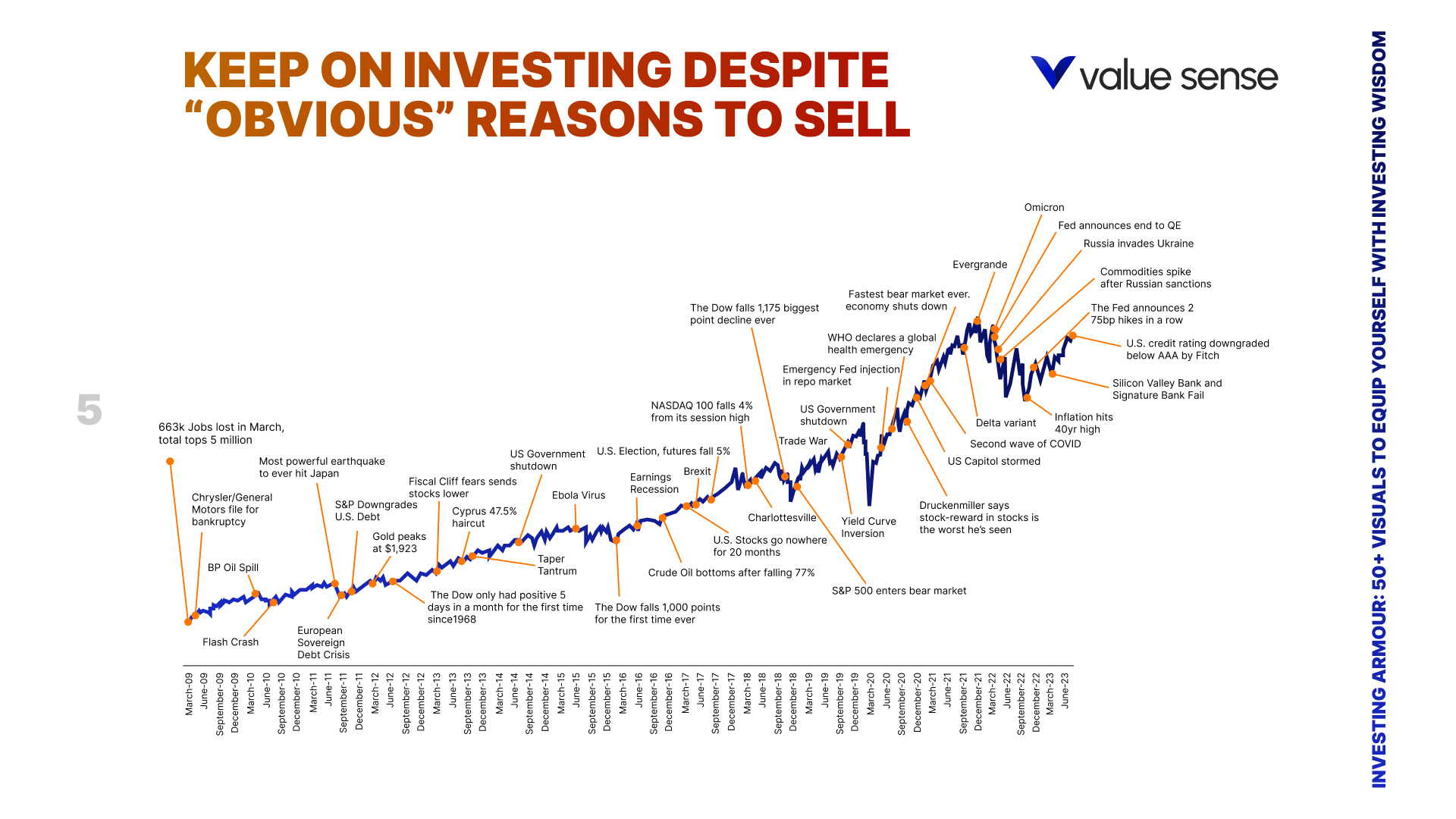
Value investing is more than just numbers and business valuation — it’s a test of psychological discipline. Successful investors understand the importance of staying calm during market turbulence and sticking to their strategy. I remember the story of a student who criticized me for being wrong about Tesla, despite the student not mentioning fundamentals or cash flow. This highlights the common mistake of allowing emotions to overshadow logic in investment decisions.
Consistency and Strategy in Value Investing
The Importance of Patience
Patience is perhaps the most underrated skill in investing. Value investing requires a long-term commitment, often waiting years for stocks to reach their intrinsic value. Many newer investors expect instant gratification, growing frustrated when stocks don’t immediately rise in price.
WHAT'S THE EASIEST WAY TO VALUE STOCKS AND FIND INTRINSIC VALUE?
At Value Sense, we've integrated the most trusted methods for valuing stocks to automatically calculate intrinsic value. This includes a combination of the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) model, Relative Valuation, and the 52-week low analysis for a comprehensive approach.
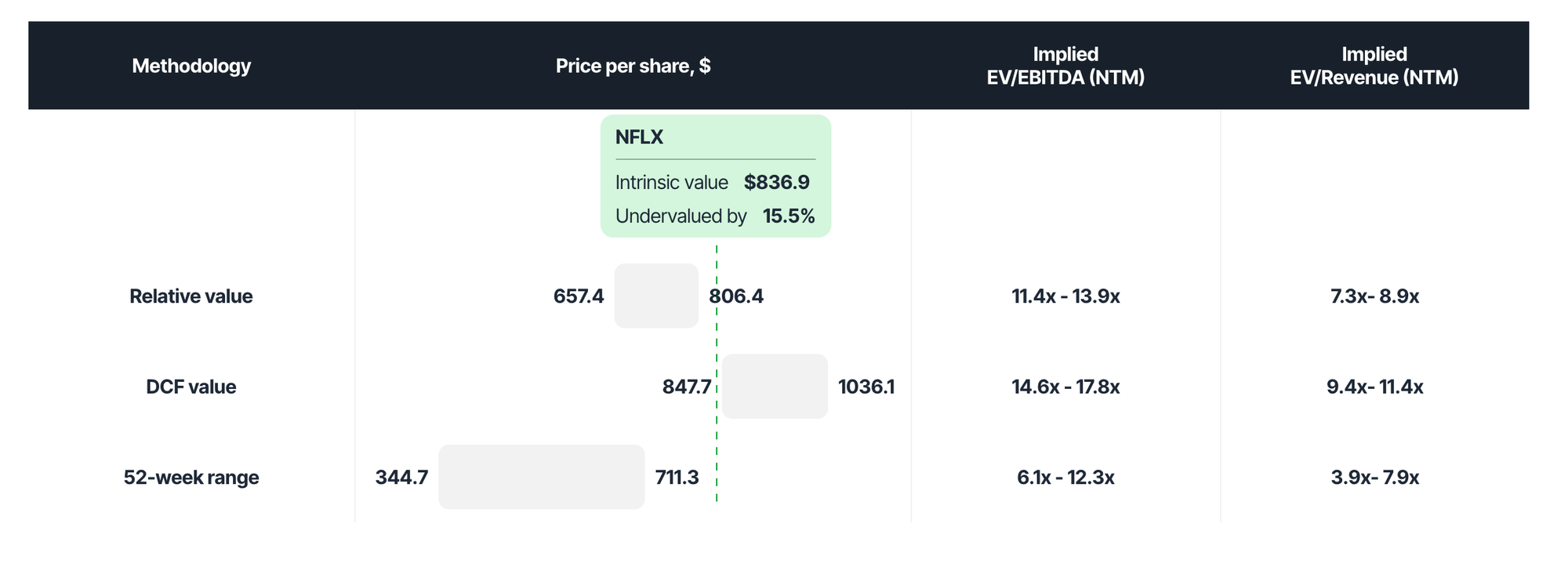
We also have 10 easy-to-use value investing calculators that help you understand stock valuation better:

- Earnings Growth Model: Projects future earnings growth to estimate a stock's value.
- Discount Rate: Calculates the rate used to discount future cash flows back to present value.
- Peter Lynch Fair Value: Uses a formula based on earnings growth to determine a fair price for a stock.
- Ben Graham Fair Value: Applies classic valuation principles to find the intrinsic value of a stock.
- Peter Lynch Charts: Visual tools that display historical performance and growth metrics to aid decision-making.
- Intrinsic Value Calculator: Provides a quick estimate of a stock’s intrinsic value based on key financial metrics.
- Earnings Power Value (EPV): Assesses the sustainable earning power of a business to establish its value.
- Reverse DCF: Works backward from the current stock price to find out what growth rate the market expects.
- Relative Value: Compares valuation metrics of similar companies to identify undervalued stocks.
- DCF Value: The DCF method is used to determine the present value of expected future cash flows.
With these tools, you can easily evaluate stocks, make informed investment decisions, and enhance your value investing strategy.
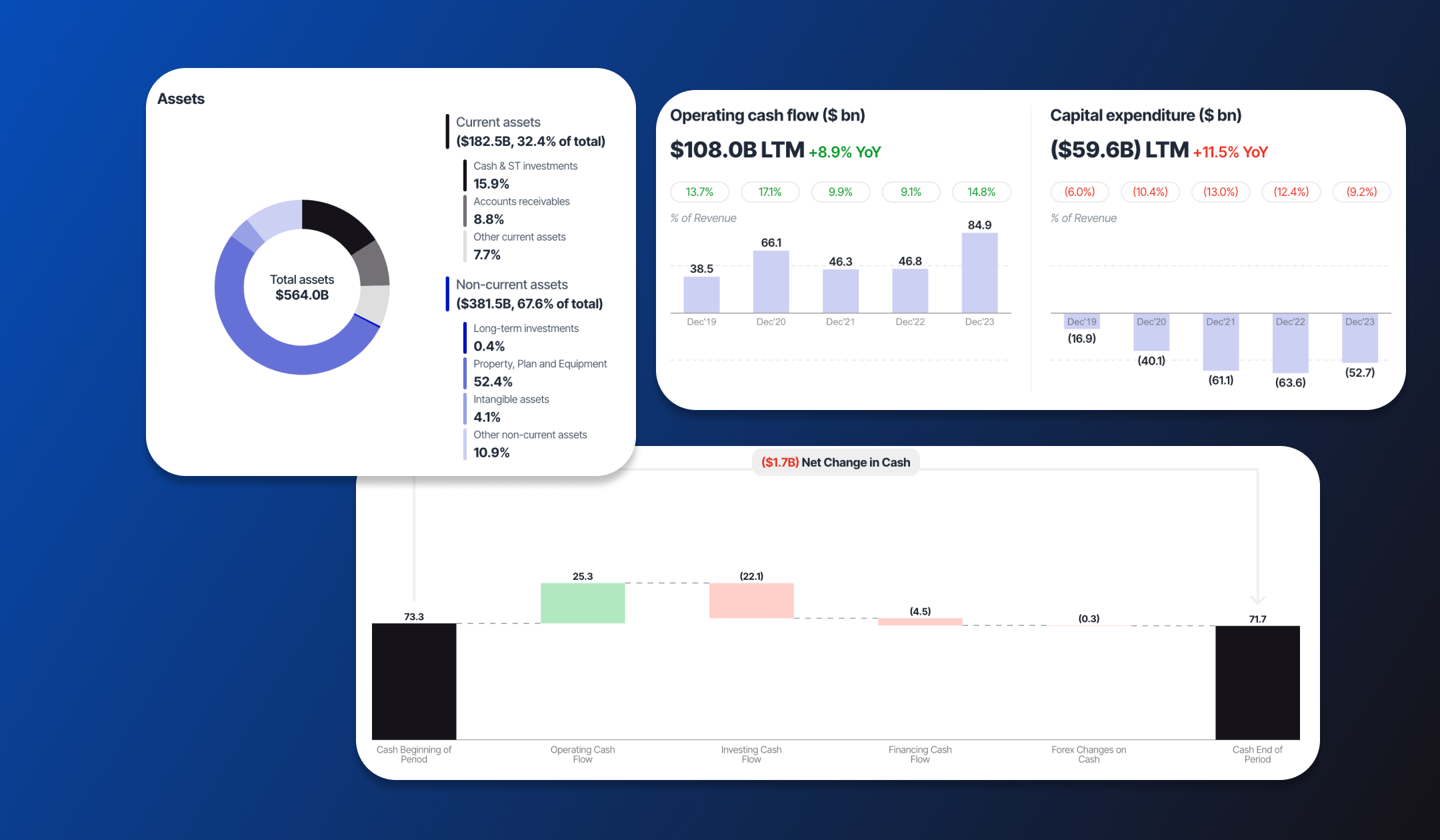
Value Sense helps you understand all companies' financial data, and provides essential tools.
- Historical Financial Analysis - Discover key financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Financial ratios - get access to the most important financial ratios
- Dividends analysis - understand how often a dividend is paid, get dividend yields, and find stocks with growing dividends.
- Comparison analysis - stock competitors, stock price compare, stocks comparison charts, all in one tool for stock comparison.
For those seeking market opportunities, our analytics team has compiled over 10 exclusive lists of undervalued and high-quality stocks:
Ready to start?
Join 3,500+ value investors worldwide
